This blog will share some key information about physics Atoms and Radioactivity to help you understand easier!
Table of Contents
- Simple atom model
- Numbers within the atom
- Nuclear radiation
- Types of radiation
- Measuring radiation
- Nuclear energy
- Radioactivity uses
Simple atom model :
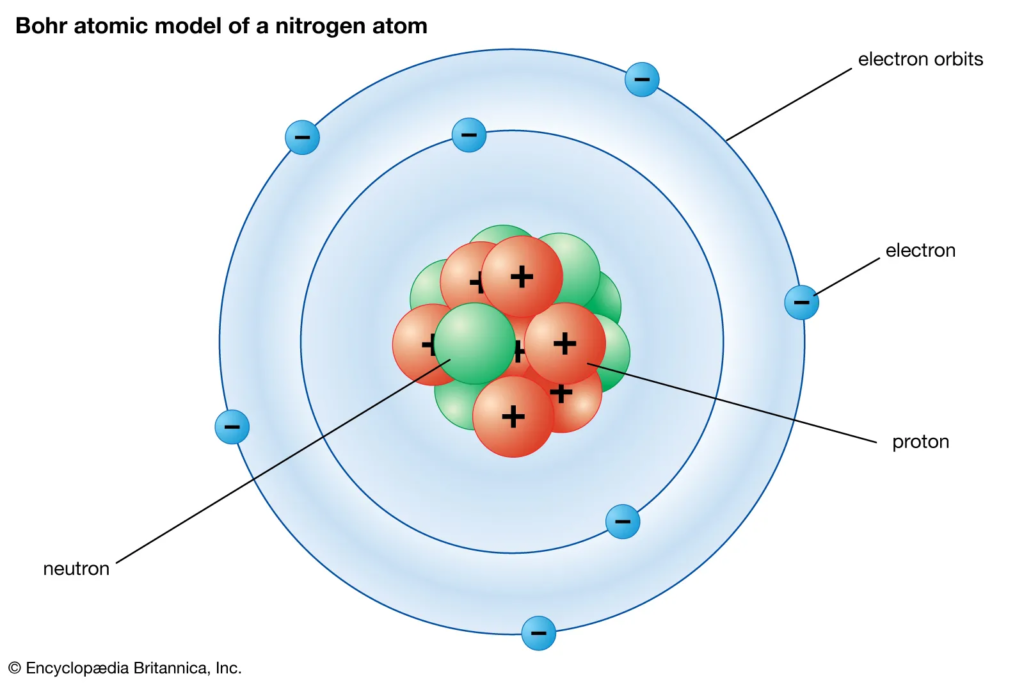
There are 3 main particles of an atom :
- Proton : has a positive charge (+), can be found within the nucleus of the atom
- Neutron : has no charge, can be found within the nucleus of the atom
- Electron : has a negative charge (-), can be found in the shells of the atom
The atom can be separated into 2 main part :
- Nucleus : It is made up of protons and neutrons, The protons and neutrons are bound together called “strong nuclear force”.
- Shells : Shells of an atom are formed when there are electrons present. Electrons in the shells orbit around the nucleus at a high speed. They are held in orbit around the nucleus due to the opposite charges of the protons and electrons.
Numbers within the atom
The number of particles would depends on what atom it is.
The “type of atom” is called an element. It is the simplest form of a substance that cannot be broken down into simpler forms.
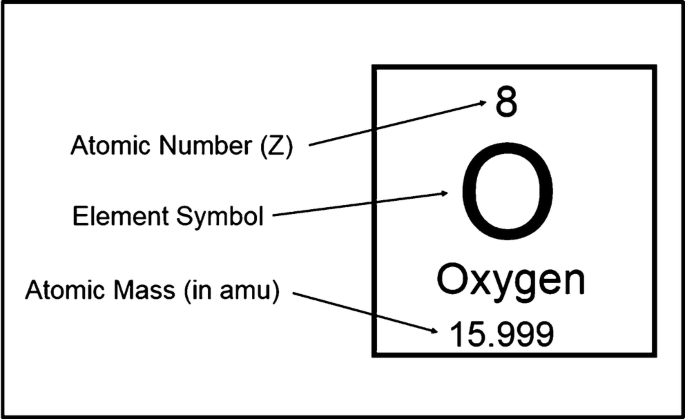
- Atomic number : The number of protons in the atom of an element, this would determine the element of the atom
- Mass number/nucleon number : The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. proton number + neutron number = mass number
Not all atoms of the same element are exactly alike, some have more neutrons than others. These are called isotopes. It is when atoms of the same element have different neutron numbers.
Electrons reside in shells surrounding the nucleus, as mentioned before, these shells are fixed levels around the nucleus and a shell can only hold certain amounts of electrons. (2,8,8,8,….and so on). These shells and electron within these shells will determine the chemical properties and chemical bonds of the atom. Elements with similar electron configuration would have similar chemical properties.
Nuclear radiation
Some materials contain atoms with an unstable nucleus. As time passes, the unstable nucleus starts to break down and thus, shoots out tiny particles from it and in certain cases they shoot out bursts of energy as well.
They can be referred to as “nuclear radiation” as the particles and waves “radiate” from the nucleus. Materials that emit this are called radioactive and the disintegration or breaking down of the nucleus is called radioactive decay.
Half-life radiation – the amount of time it takes for half of the nuclei sample to decay.
Types of radiation
- alpha particle
- 2 protons and 2 neutrons
- +2 relative charge
- relatively large mass
- up to 0.1 of the speed of light
- strong ionization
- does not penetrate very well, can be stopped by a thick sheet of paper or a few cm of air
- can be deflected by magnetic and electric fields
- beta particle
- an electron
- -1 relative charge
- relatively low mass
- up to 0.9 of the speed of light
- weak ionizing effect
- more penetrating than an alpha particle but can still be stopped by a few mm of metal
- can be deflected by magnetic and electric fields
- gamma rays
- electromagnetic waves
- 0 relative charge
- no mass
- as fast as light
- very weak ionizing effect
- very penetrating, never completely stopped but the intensity can be weakened by thick lead or concrete
- does not get deflected by magnetic or electric fields
Ionizing radiation
Ions are charged atoms, they become ions when they lose or gain electrons. Nuclear radiation can remove electrons from the atoms in their path, so it has an ionizing effect.
Measuring Radiation
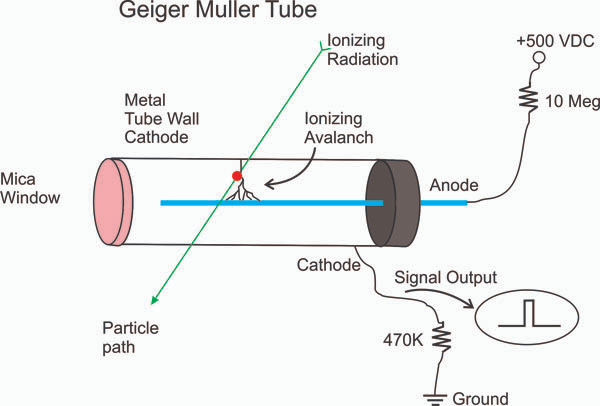
https://www.imagesco.com/geiger/geiger-counter-tube.html
- Geiger-Müller tube
- This can be used to detect alpha, beta, gamma radiation
- A GM-tube can be connected to the following :
- A ratemeter
- A scaler
- An amplifier and loudspeaker
Nuclear energy
- Fission
- the nucleus of an atom becomes highly unstable and shoots out fragments, splitting the atom. This is called fission
- energy is released in this process
- If emitted neutrons hit another atom and go on to split another nuclei and so on, this is a chain reaction and would cause large amounts of energy to be released.
- Fusion
- When two nucleuses join together to form a heavier nucleus. This is called fusion
- It is the process that powers stars
Radioactivity uses
- tracers
- testing for cracks
- carbon dating – study how old animals and plants are using half life
- dating rocks – studying the age of rocks using half life


