Table of Contents
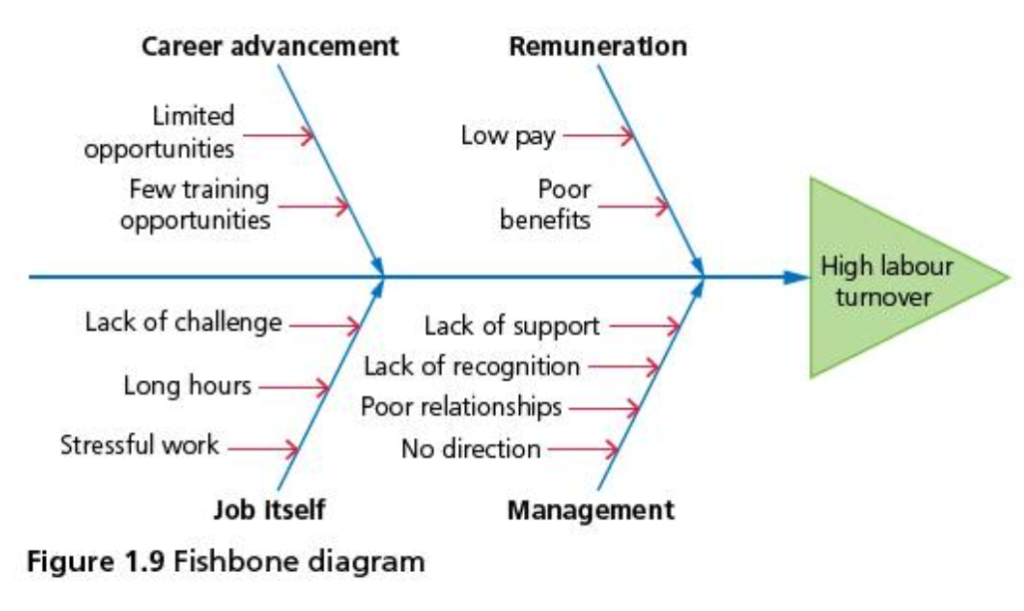
Fishbone diagram
It is a graphical representation of the most likely causes and effects of an important decision. It was devised in the 1960s by Japanese quality guru Professor Kaoru Ishikawa. As a qualitative organizational planning/decision-making tool, the fishbone diagram is used to identify the root causes (shown as bones) of a problem (shown as head of fish).
Example
Overall Basic Structure
Explanation
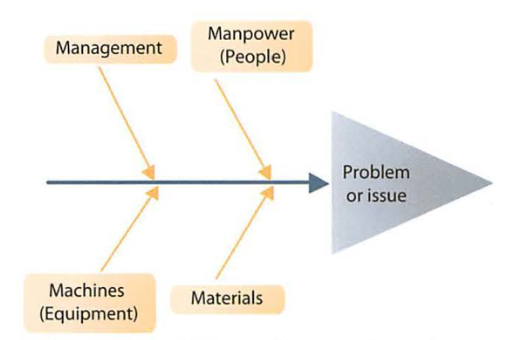
The 4Ms (management, manpower, machines and materials) is one method that can be used to identify different categories of causes of a problem or an issue, such as demotivated or unproductive employees.
Manpower refers to the labor management, e.g. unskilled workers, a lack of training and insufficient
Management, e.g. unsuitable management style and miscommunication with the workforce,
Machines refers to the capital involved in production processes, technological failures, faulty equipment and the use of outdated machinery
Materials refers to the raw materials needed to ensure that production can be carried out, e.g. sub standard (poor quality) materials and delayed deliveries.
To successfully construct a fishbone diagram, the following steps must be observed:
- the problem or issue must be clearly stated and agreed upon before futher discussion begin
- contributors must be concise and to the point. Causes rather than symptoms must be stated.
- for each bone, brainstorm the possible causes and locations these ont the node
- consider combining nodes that are rather empty or scrapping them altogether
- consider separating overcrowded nodes
- consider which root causes warrant further investigation by circling these on the diagram
- discuss how each circled item affects the problem or issue being investigated
- once the root causes have been established, the fishbone is complete and decision makers move on to devising appropriate strategies to deal with in businesses
However, the fishbone diagram model tends to be rather simplistic for some real world problems. In practice, the fishbone diagram is often used in conjunction with other decision-making frameworks to establish the root (causes) of a problem.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Fishbone Diagram
| Advantages of fishbone diagram | Disadvantages of fishbone diagram |
| It shows a variety of probable causes of a given problem in a concise way | Causes and effects are not always interrelated, making the construction of the fishbone more difficult and less meaningful |
| As a visual tool, it is easy to follow in order to determine the root causes and consequences of a problem or issue | As a qualitative decision-making tool, it does not include quantifiable data so its i difficult to ascertain how much each factor actually contributes to the problem |
| It organizes the causes of a problem by themes, such as communication issues or motivation problems, thus aiding the decision-making process | Similarly, it does not show which decisions or actions need to be prioritized |
Decision Trees
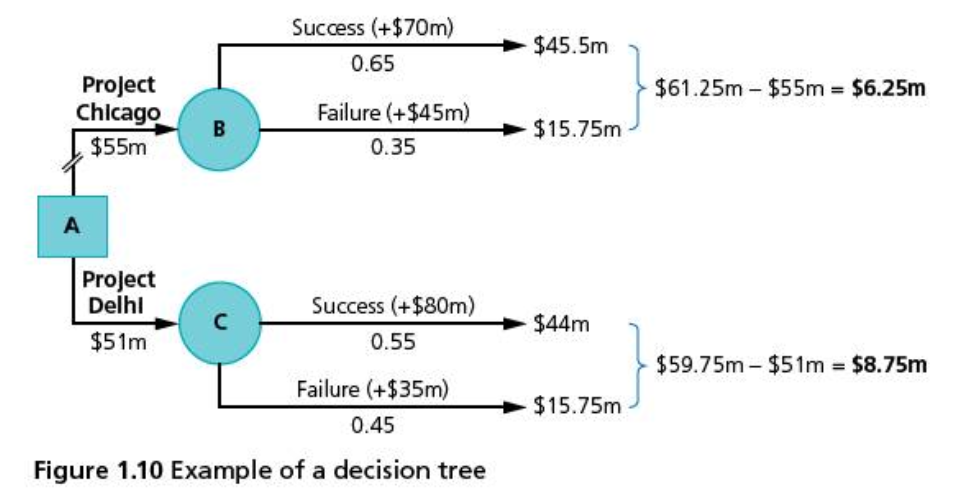
A decision trees is a quantitive and systematic decision-making tool that allows managers to visualize possible options and their probable outcomes. The tool allows managers to calculate the expected value of each decision in order to plan the best option to follow.
The diagram is constructed from left to right:
- decision nodes = shown as squares
- chance nodes = shown as circles
- probability of the different outcomes for each chance node
- actual values of each outcome are stated at the end of each branch
- each unwanted branch of the decision tree is cut off (rejected), indicated by two parallel lines
Example
Explanation
- Probabilities of various outcomes are shown, e.g. 0.35 means there is a 35% chance of the outcome actually materializing.
- Probabilities for each chance node must add up to 1.0, i.e. 100% likelihood.
- The figure above illustrates the decision of a firm to pursue either Project Chicago which costs $55m or Project Delhi which costs $51m.
Main Points
- There is a 65% chance of success if the firm chooses Project Chicago, which would gain the firm $70m in sales revenue. Thus, the likely outcome is $70m x 0.65 = $45.5m
- There is a 35% chance of failure or Project Chicago, with expected revenues of only $45m. Hence, the probable outcome is $45m x 0.35 = $15.75m
- Therefore, the combined outcome for Project Chicago is $45.5m + $15.75m = $61.25m. After the costs of the project are accounted for, the likely yield of Project Chicago is $61.25m = $55m = $6.25m
- For Project Delhi, there is a 55% chance of success in earning $80m. Hence, the likley outcome is $80m x 0.55 = $44m
- If the project fails, teh likley outcome of earning $35m in sales revenue is $35m x 0.45 = $15.75m
- Hence, the combined likely outcome is $44m + $15.75m = $59.75m. The likely profit is therefore $59.75m – $51m = $8.75m
Conclusion
- Two parallel lines that cross through a branch represent the options that are rejected based on quantitative grounds
- Examining the decision tree in the figure above shows that Project Delhi should be pursued.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Decision Trees
| Advantages of decision trees | Disadvantages of decision trees |
| They allow managers to set out problems in a clear and logical manner | The probabilities given in a decision making |
| All potential options can be seen at the same time, thereby speeding up decision making | They are based on quantitative |
| They consider the risks involved in decision making, such as possible negative outcomes | The technique does not necessarily reduce the amount of risk involved in decision-making |
| As a visual stimulus, they provide a tangible insight to a problem, rather than having to rely on people’s views/emotions of the problem | Delays in the planning process can void the data by the time a decision is actually made, yet time lags |
| They enable more scientific and objective decisions to be made as at all likely costs of decision are considered |
Example Question #1
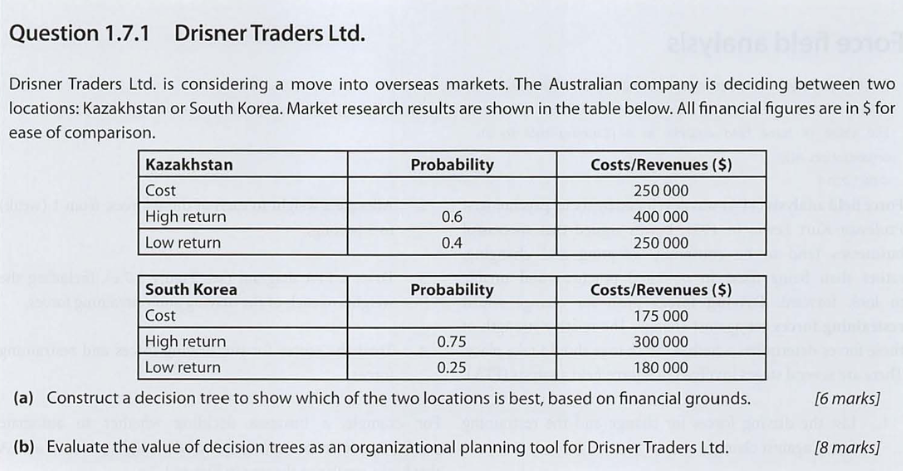
Answer
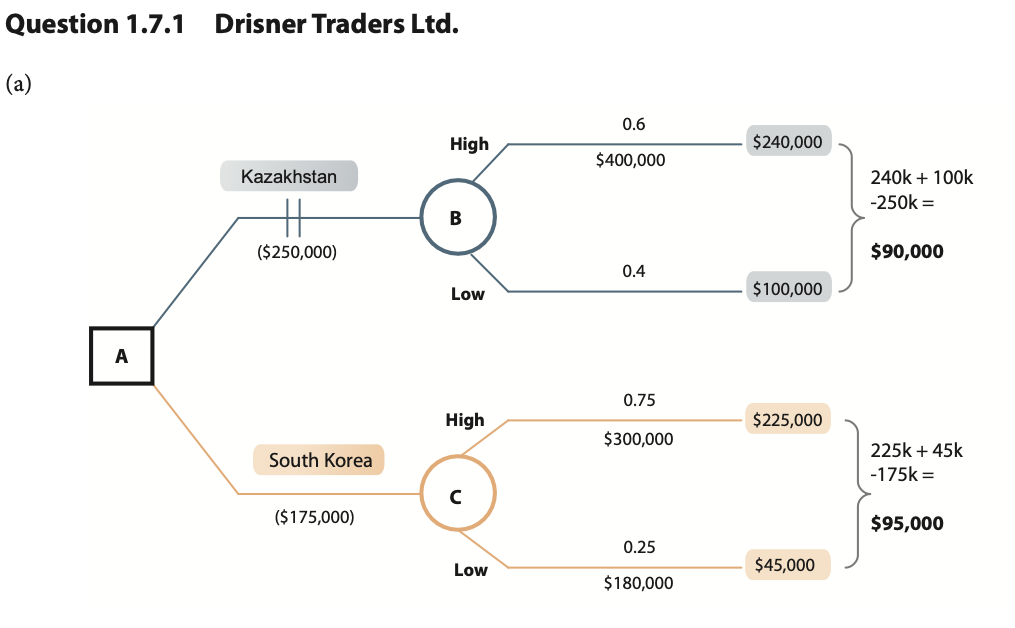
Award 1–3 marks for using a decision tree framework which shows some attempt at calculating the expected values, but the answer is incomplete and/or inaccurate.
Award 4–5 marks for a complete decision tree although there are one or two minor errors.
Award the maximum 6 marks if the candidate shows a fully labelled, complete and accurate decision tree, including the working out to calculate the expected values. There is clear identification of which of the two options is the best choice, i.e. South Korea.
(b) Decision trees allow:
- Drisner Traders Ltd. to gain a broad idea of possible outcomes of the project/decision, i.e. in this case the choice of two locations
- Easier interpretation of the decision to prevent misunderstandings or confusion Easy and straightforward calculations to aid decision-making
- Easy accessibility for all users to make rational/scientific decisions
- Provide a quantitative tool in decision-making.
However, decision trees:
- Are based on estimated figures only and the actual outcomes may well be very different
- Can be inaccurate unless all costs, benefits and possibilities are considered
- Only consider quantitative issues in decision-making, so might be considered too simplistic a model
- Qualitative factors could be examined, e.g. familiarity with the two different locations, availability of skilled labour, recruitment and training concerns, cultural issues, legal issues, tax systems or simply management preferences
- Similarly, other quantitative methods could be considered, e.g. investment appraisal to see which location would generate the greatest financial return
- Other decision-making tools might also be useful to Drisner Traders Ltd. such as force field analysis (in order to minimize any resistance to change) and/or STEEPLE analysis
Award 1–2 marks for a vague and generalized answer. The answers may appear in bullet-point form with no or little development.
Award 3–4 marks if only advantages or disadvantages of decision trees are examined.
Award 5–6 marks if both the advantages and disadvantages of decision trees are considered. At the top end, there is an attempt at application using the case study.
Award 7–8 marks if both the advantages and disadvantages of decision trees are considered, with clear application and evidence of evaluation of the usefulness of decision trees for Drisner Traders Ltd.
Example Question #2
Answer
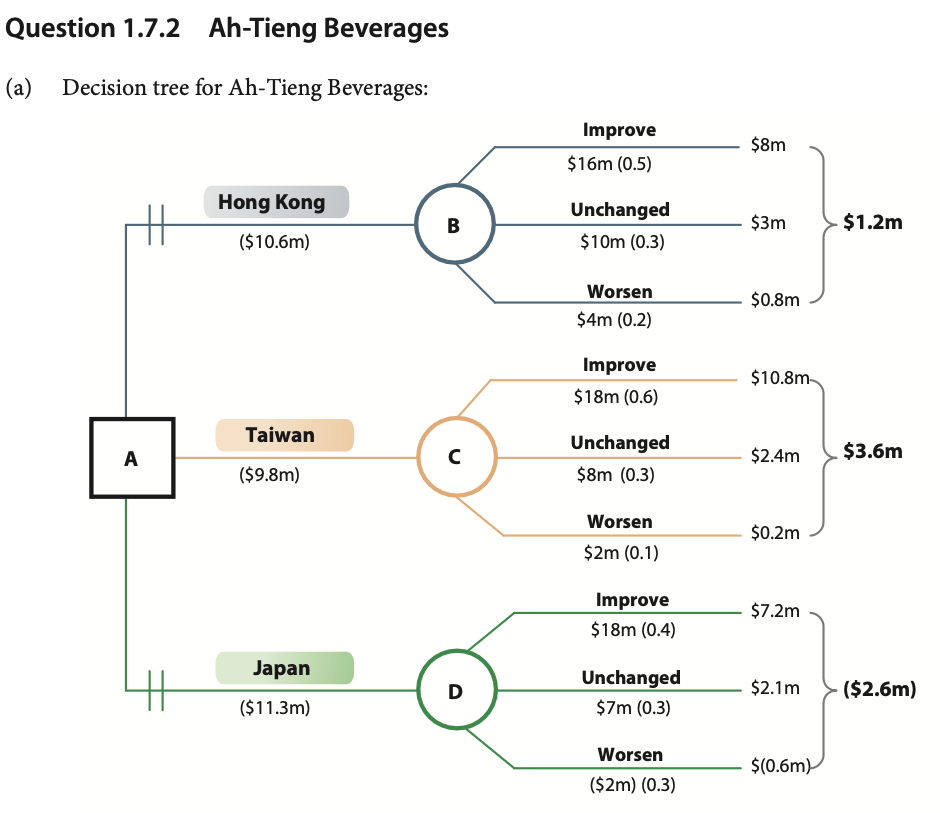
Award 1–2 marks for using a decision tree framework which shows some attempt at calculating the expected values, but the answer is incomplete and/or inaccurate.
Award 3–4 marks for a complete decision tree although there are one or two minor errors.
Award the maximum 5 marks if the candidate shows a fully labelled, complete and accurate decision tree, including the working out to calculate the expected values. There is clear identification of which of the three options is the best choice, i.e. Taiwan.
(b) The benefits of using decision trees to organizations such as Ah-Tieng Beverages include:
- Requires a formal and objective analysis of the various options for, and possible outcomes of, expansion in overseas markets
- Requires full consideration of the financial costs and outcomes of the decision, thereby allowing the board of directors at Ah-Tieng Beverages to assess the level of financial risk involved with each possible outcome
- As a systematic decision-making tool, decision tree analysis allows managers at Ah-Tieng Beverages to make strategic decisions without subjectivity
- Decision trees are quite easy to construct and simplistic to interpret. Managers at Ah-Tieng Beverages are able to understand decision trees with brief but succinct interpretations.
However, the outcome and value of decision trees are only as good as the quality of the data used by Ah-Tieng Beverages to produce the decision tree. If the quantitative data is inaccurate (e.g. due to management bias or use of outdated information), then the outcome of the decision tree becomes less reliable.
Furthermore, decision trees ignore qualitative factors that can influence decision making.
Award 1–2 marks if the answer is vague, generalized or lacks substance.
Award 3–4 marks if the answer shows some understanding of the use of decision trees, although it might lack detail or be unbalanced. Application is likely to be missing.
Award 5–6 marks if there is consideration of both the usefulness and limitations of decision trees. Appropriate terms and examples are used.
Award 7–8 marks if there is a balanced discussion of both the usefulness and limitations of decision trees for Ah-Tieng Beverages. Appropriate business management terminology and examples are used. There is evidence of critical thinking and evaluation, written in the context of the case study.
Force Field Analysis
Force Field Analysis (FFA) was devised by German-American psychologist Kurt Lewin as a planning and decision-making tool for examining the factors for and against change.
Driving forces are factors that support change towards a certain goal.
Restraining forces are factors that block or hinder change.
These factors/forces are numerically weighted in order to calculate the relative strengths of driving and restraining forces, so that they can aid in decision-making in an objective and quantifiable way.
The weights range from 1 to 5, with 5 being of most significance to the business. In the example below. as the driving forces outweigh the restraining forces, the objective decision is to relocate the business.
Example
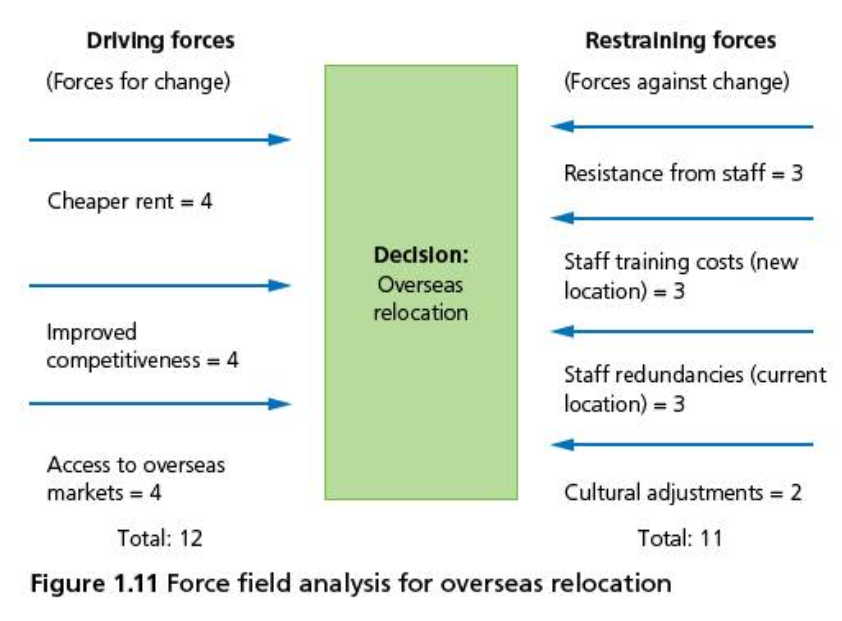
Advantages & Disadvantages of Force Field Analysis
| Advantages of FFA | Disadvantages of FFA |
| As a quantitative planning tool, it makes the decision-making process more objective and logical | Qualitative factors affecting decision making are ignored or difficult to quantify |
| It offers a simple visual representation of the factors/forces for and against change | The omission of certain driving or restraining forces can alter the outcome quite drastically |
| Weighting (numerical values) the forces makes managers consider the relative importance of factors affecting the decision | The weighting of the forces is subjective, leaving room for potential bias |
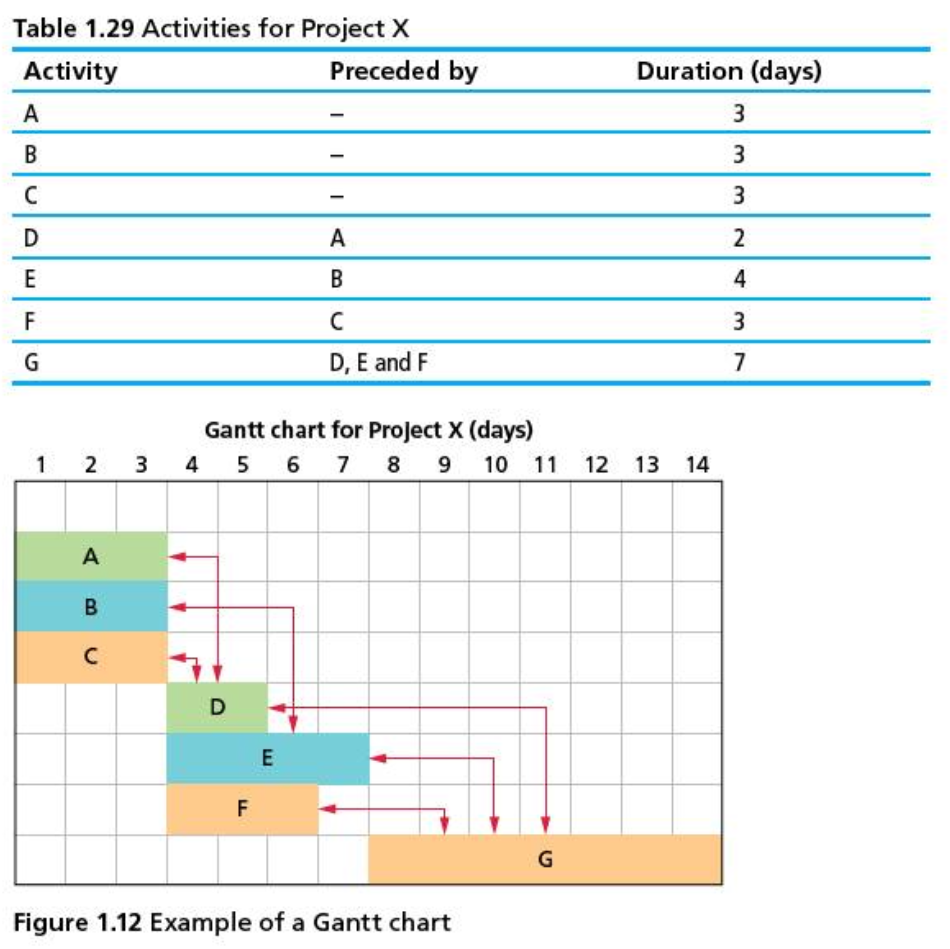
Gantt Chart
A Gantt Chart, devised by Henry L. Gantt, is a visual planning tool that illustrates the sequencing and schedule fo a particular project. It ultimately helps project managers find out how long a project should take to complete.
Links established between dependent tasks allow managers to sequence the various activities (tasks) of a particular project and shows what must be completed before the next task can begin.
Example
Advantages & Disadvantages of Gantt Chart
| Advantages of Gantt Chart | Disadvantages of Gantt Chart |
| Show the dependencies between different activities in order minimize the time needed to complete a project | The length of time (each bar) does not necessarily correlate with the amount of work or resources involved for each activity |
| There are wide applications, e.g. scheduling production processes, employee work rosters, and holiday schedules | Need to be monitored and may need regular updating |
| Help managers to set realistic deadlines for the various activities of a project | Complex projects may be difficult to display on a one-page Gantt chart |
| Simple to interpret and understand | Its simplicity means that a Gantt chart may not provide enough detail or information for complex projects |
| Allow managers to monitor progress and take corrective measures | Based on and reliant on the estimates of the timings of each task |
Example Question #1
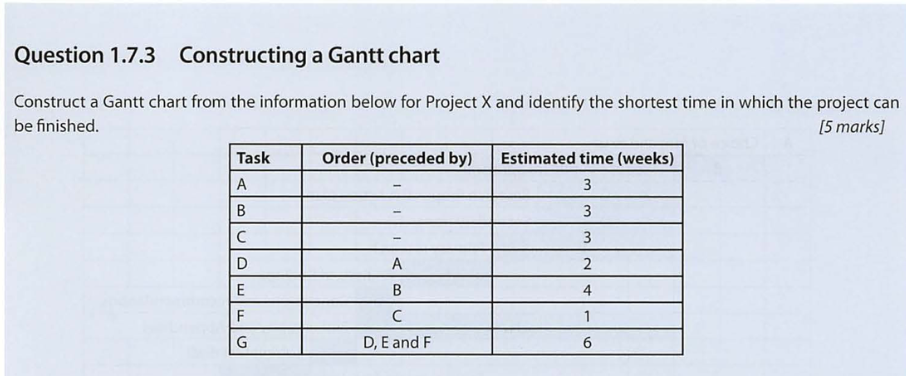
Answer
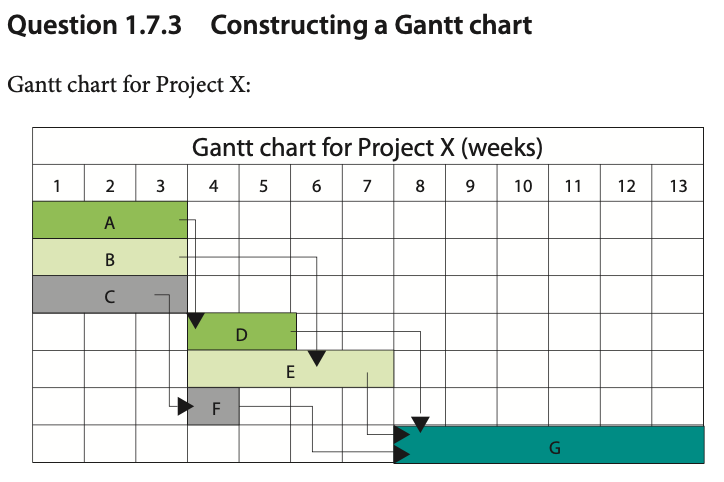
Example Question #2

Answer
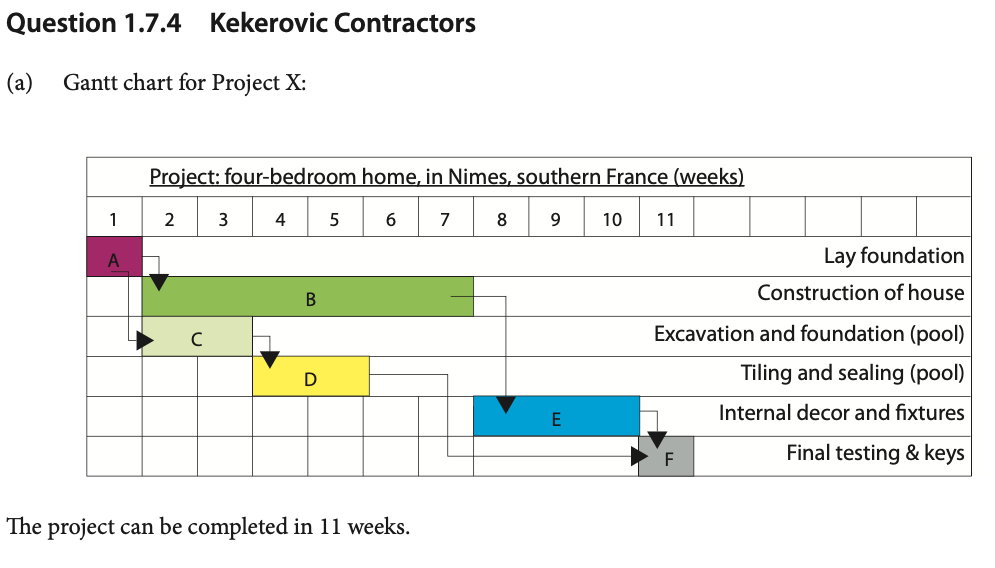
Award 1–2 marks for constructing a Gantt chart that shows some understanding, but the answer is incomplete and/or inaccurate.
Award 3–4 marks for a complete Gantt chart although there are one or two minor errors.
Award the maximum 5 marks if the candidate shows a fully labelled, complete and accurate Gantt chart. There is clear identification of shortest duration in order to complete the project i.e. 11 weeks.
(b) The use of a Gantt chart can be important for businesses such as Kekerovic Contractors for several reasons, such as:
- It encourages forward planning at Kekerovic Contractors, i.e. managers need to consider the different aspects of the construction project in order to complete it in minimal time.
- Since a Gantt chart provides a visual stimulus, it is easier to interpret the logistics of the development in order for the construction project to run more smoothly.
- It identifies the shortest time in which the construction project can be completed so that the buyer will have the house completed on time.
- Gantt charts can help Kekerovic Contractors to control costs more effectively by identifying when certain activities can start and how long certain tasks within a project should last.
- It helps to keep project managers accountable in case there are delays. This is important for the efficient running of the business.
- Ultimately, the tool allows managers at Kekerovic Contractors to complete the project successfully in the quickest time available by overseeing all the various activities and ensuring that each task is completed on schedule.
Award 1–2 marks if the explanation is incomplete and/or vague. It might be presented as a list that is unexplained.
Award 3–4 marks if the explanation is thorough and good examples are used in the context of the case study. There is no need to include more than two reasons for maximum marks.
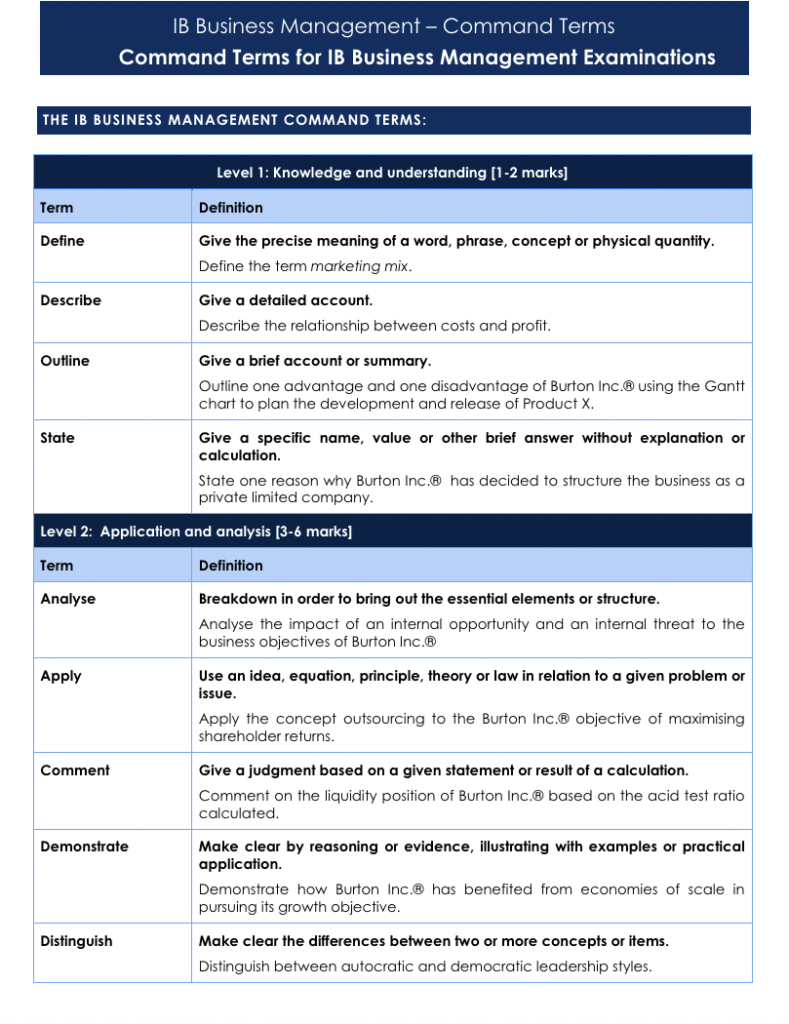
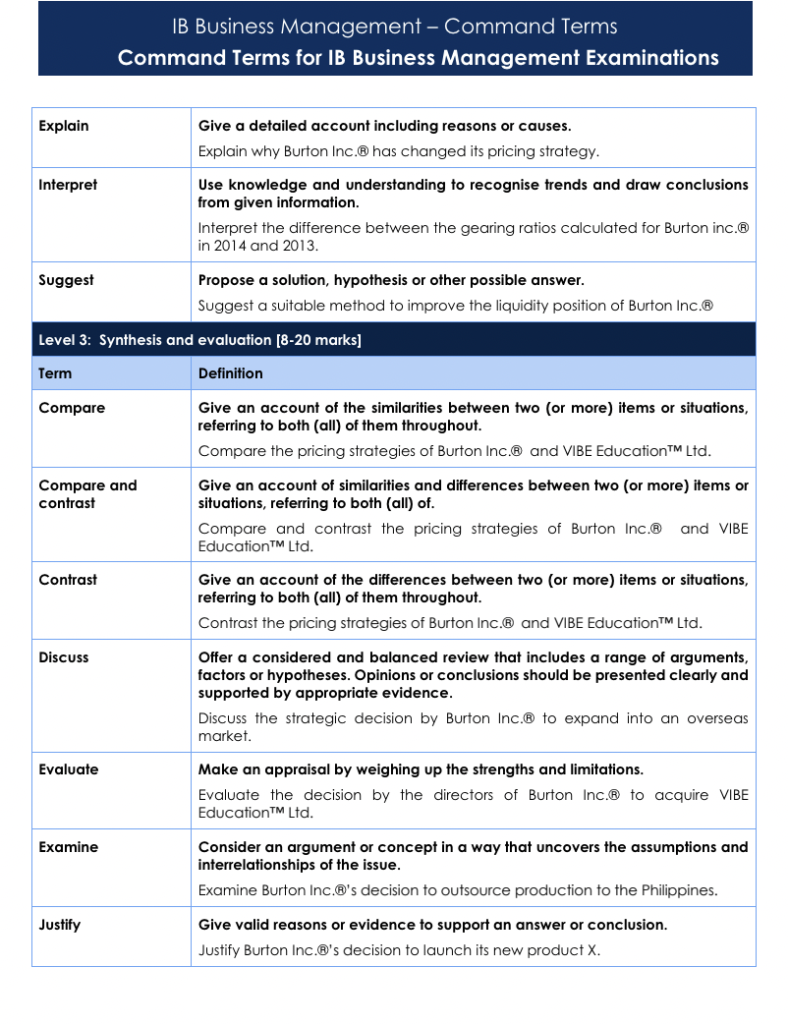
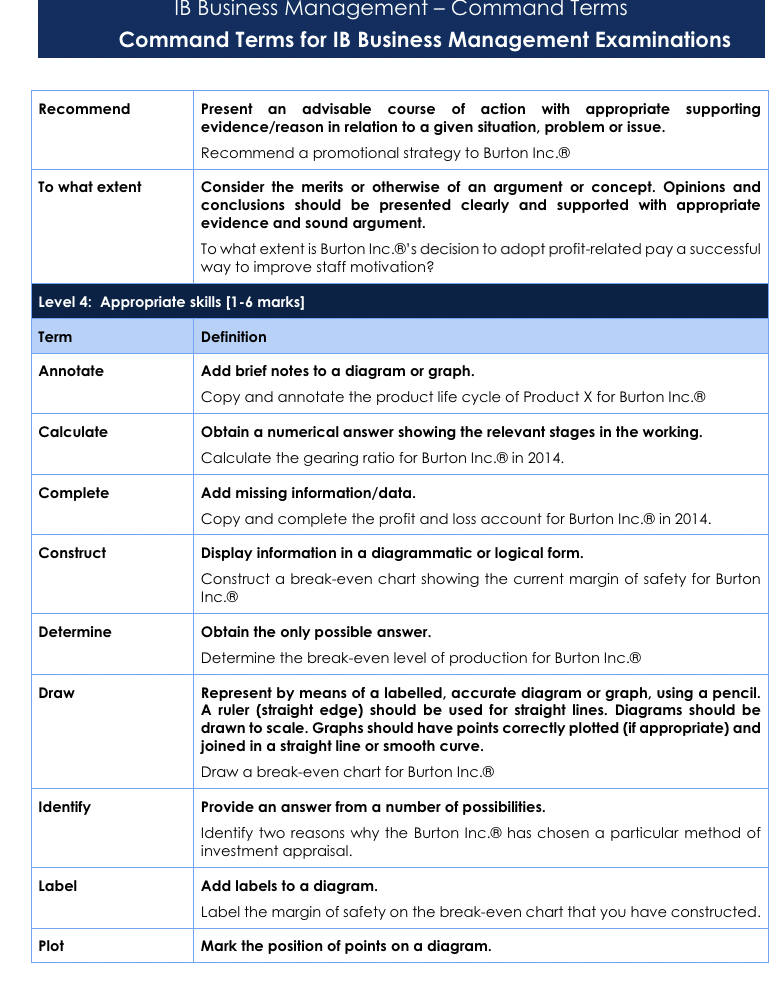
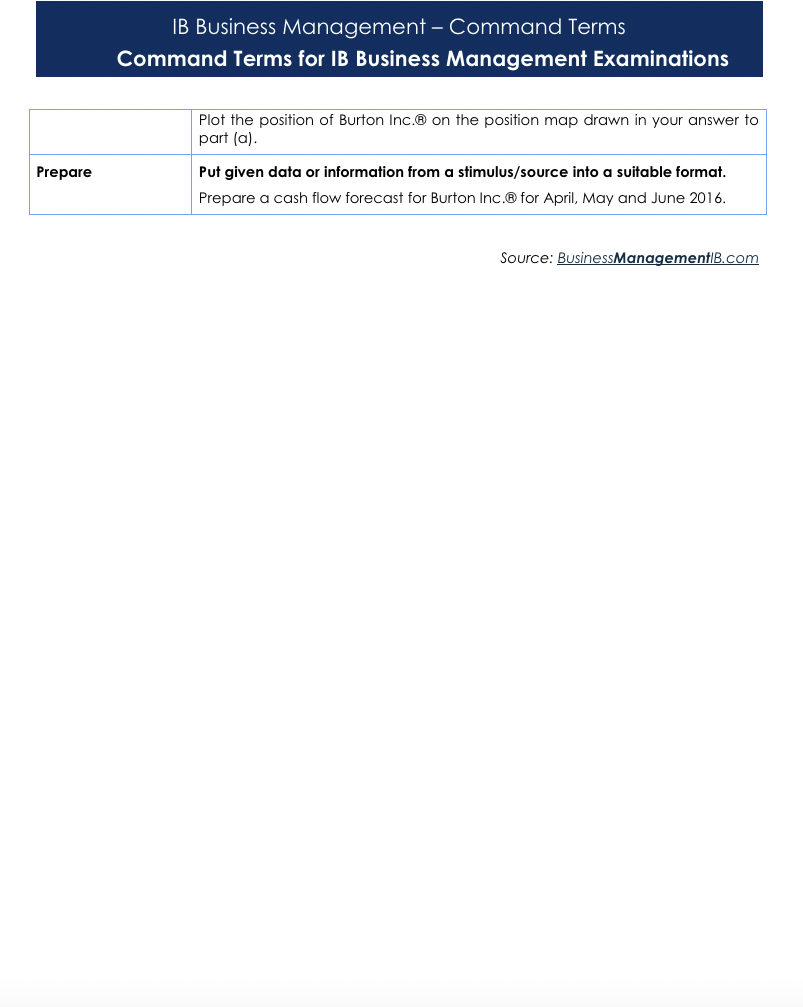
Command Terms
References
- https://www.amazon.com/International-Baccalaureate-Business-Management-Hoang/dp/1921917245
- https://www.amazon.com/Business-Management-Diploma-Study-Revision/dp/1471868427
- https://www.ibbookshop.co.uk/product/business-management-answer-book-for-3rd-edition-downloadable-pdf/



