Table of Contents
- The Integrated Relationships Of Concepts, Content And Contexts In Business Management
- 6 CUEGIS Concepts
- Working With A Conceptual Approach
- Answering Section C (Paper 2)
- IMPORTANT
- Assessment
- Assessment Criteria
- Questions From Previous Years
- Examples Of CUEGIS Concept Essays On Real-World Organizations!
- References
- Click Here To Read More About Assessment Criteria!

Concept-based learning (CBL), as defined by education consultant Dr. H. Lynn Erickson, is a three-dimensional model that frames facts (content) and skills with concepts of the Business Management course – change, culture, ethics, globalization, innovation and strategy.
The rigor of the Business Management course creates two approaches to teaching and learning: either students can be told what they need to know (based on factual knowledge and skills in Business Management) or teachers can get their students excited enough to discover and deepen their understanding of Business Management for themselves.
The Integrated Relationships Of Concepts, Content And Contexts In Business Management
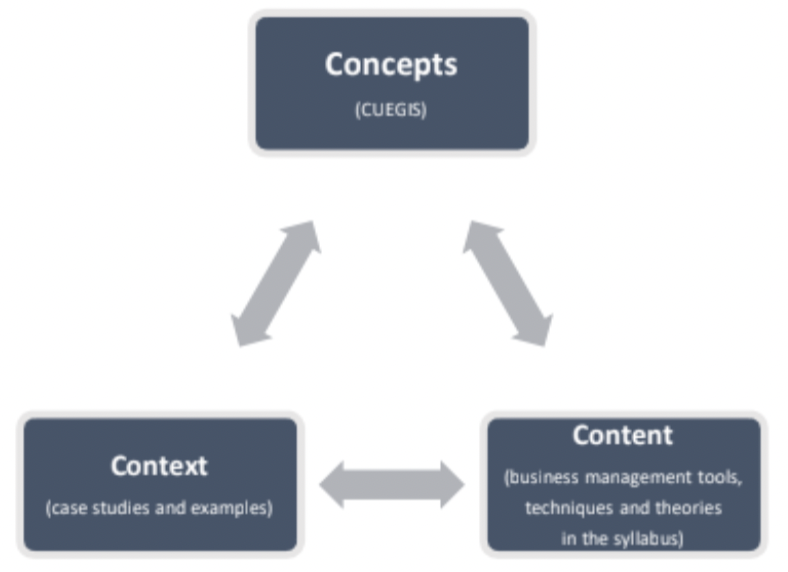
Concepts are anchored in the tools, techniques and theories of the subject and come alive through case
studies and examples. Together, these help you to acquire a holistic and integrated understanding of business management.
6 CUEGIS Concepts

Change
The adaptation of the organization to accommodate for the external business environment, e.g. organizations need to adapt what they do in relation to new technologies, social and cultural factors, changing demographics, different government laws, economic trends and globalization.
Competition, new technologies and markets, and trends in consumer behavior lead business organizations to adapt their objectives, strategies and operations.
Success emerges from the ability to research and respond to signals in both the internal and external environment.
Culture
An organization’s traditions and norms, i.e. the way in which things are done within an organization. It can also be referred to as the customs and norms within a certain area, region or country, which can have a direct impact on all aspects of an organization’s operations.
Every organization operates in a range of environments in which its role may be interpreted differently. These expectations affect planning, decision-making and strategy implementation.
Within an organization, values and backgrounds influence what stakeholders focus on and how they work.
Ethics
A set of moral values and guiding principles that influence how individuals, organizations and societies behave. Different stakeholders may have different perspectives on what is considered ethical business behavior.
Every business decision has moral implications.
These consequences can be significant for internal and external stakeholders and the natural environment.
Globalization
It is the ongoing process of interaction and integration between people, firms and organizations trade is conducted over widening geographical boundaries, offering opportunities and threats.
A wide range of international forces (such as the increasing social, cultural, technological and economic integration) influence business organizations. In turn, business organizations shape these forces.
Many business organizations operate across national boundaries. Even local businesses and consumers are influenced by global forces.
Innovation
It refers to the incremental or radical process of improving business, such as introducing new or adapting existing technologies to supply improved goods or services.
Incremental or radical improvements to a business idea, or the generation of new ideas in relation to a final product, service or process, are the result of internal or external influences.
For many business organizations, a key challenge is bringing in “the new” and managing the process of improvement in a sustainable way.
Strategy
Strategy is the long term plan and decisions which allow an organization to achieve a particular organizational goal.
Strategy refers to the significant long-term planning decisions that organizations make in order to meet the needs and wants of their stakeholders.
Strategy is about asking questions: what, why, when, how, where and who?
Working With A Conceptual Approach
Working with a conceptual approach prepares you for a part of your assessment. The six concepts are a part of the formal assessment of the course at both SL and HL.
In your Paper 2 (Section C), you will be asked to use two of the six concepts to discuss the situation and issues faced by real-world organizations that you have studied during the course, making use of business management tools, techniques and theories.
Answering Section C (Paper 2)
The main focus of the questions will be on two of the six concepts – but you need to draw on your knowledge of other relevant content, concepts and contexts to answer the question.
There is no stimulus material included, so you will need to rely on your ability to apply real-world examples and case studies examined during your course and/or your Internal Assessment. You need to address the question in relation to (at least) one real-world business organization. This means you should not refer to the (hypothetical) business organization in Paper 1. You cannot use any of the
case studies in Section A and B of Paper 2 either.
As part of your holistic judgment, you should consider the perspectives of different stakeholder groups (individuals and societies) of the real-world business organization.
HL students are expected to draw on their knowledge of HL topics in the syllabus.
IMPORTANT
Do not try to write a “model” answer from an essay you have previously studied – focus instead on addressing what the actual question is asking.
Learn to integrate stakeholder perspectives throughout the essay; too often, this is done as an afterthought and superficially at the end of the essay.
For questions that asks for impacts of two concept on BM content, it is acceptable to explain that one concept may be of more significance to the organization than the other.
For Criterion C (reasoning), do not allow the examiner to ask “Why?” or “How is this relevant?
Assessment
There is no stimulus material provided for the questions.
Students are required to address the question in relation to one real-world organization but may use information from a range of sources, which may include real-world case studies examined in class and IA research. The real-world organization that students use in their response must not be the case study organization featured in paper 1.
The response should consider the perspectives of individuals and societies upon which the real-world organization impacts.
Students answer one extended response question from a choice of three.
Assessment objective level 3 (AO3) command terms are used in each question.
Each question is worth 20 marks.
Assessment Criteria
Criterion A: Knowledge and conceptual understanding (4 Marks)
This criterion addresses the extent to which the student demonstrates knowledge and understanding of the given concepts and relevant Business Management content (theories, techniques or tools, depending on the requirements of the question).
Criterion B: Application (4 Marks)
This criterion addresses the extent to which the student is able to apply the given concepts and the relevant Business Management content (theories, techniques or tools, depending on the requirements of the question) to his or her chosen real-world organization(s). The real-world organization(s) must not be the organization featured in the prescribed case study for paper 1.
Criterion C: Reasoned arguments (4 Marks)
This criterion assesses the extent to which the student makes reasoned arguments. This includes making relevant and balanced arguments by, for example, exploring different practices, weighing up their strengths and weaknesses, comparing and contrasting them or considering their implications, depending on the requirements of the question. It also includes justifying the arguments by presenting reasonable evidence or other support for the claims made.
Criterion D: Structure (4 Marks)
This criterion assesses the extent to which the student organizes his or her ideas with clarity, and presents a structured piece of writing comprised of:
- an introduction
- a body
- a conclusion
- fit-for-purpose paragraphs
Criterion E: Individuals and societies (4 Marks)
This criterion assesses the extent to which the student is able to give balanced consideration to the
perspectives of a range of relevant stakeholders, including individuals and groups internal and external to the organization.
Questions From Previous Years
With reference to an organization of your choice, examine the impact of globalization on innovation. (May 2017)
With reference to an organization of your choice, examine the impact of ethics on organizational strategy. (May 2017)
With reference to an organization of your choice, discuss the ways in which culture can promote or inhibit change. (May 2017)
With reference to an organization of your choice, examine the impact of globalization on human resources strategy. (May 2018)
With reference to an organization of your choice, examine the impact of innovation and culture on an organization. (May 2018)
With reference to an organization of your choice, examine the impact of ethics on organizational change. (May 2018)
Examples Of CUEGIS Concept Essays On Real-World Organizations!
McDonalds

Change
McDonalds regularly changes its strategy to keep up with the market demand and also to remain competitive in this large market. Over the last year, it has made many changes, for example, making major changes to its menu. Adding and removing various dishes all around the world. They also plan to add more dishes for breakfast and begin serving ‘healthy’ breakfast, every day of the month!
Culture
McDonalds has changed their company a lot according to the culture here in India. Before they decided to enter the market in India, they had decided to omit beef and pork from the menu to aid in preventing the Indian citizens from being offended. research shows that in 2003, of 100 meals that people ate in a month, only three were eaten out. They introduced a 20 rupees (20p) burger called Aloo Tikki Burger, a burger with a cutlet made of mashed potatoes, peas and flavoured with Indian spices. “It’s something you would find on Indian streets; it was essentially the McDonald’s version of street food. The price and the taste together, the value we introduced, was a hit. It revolutionised the industry in India,” he says. Now eating out has gone up to 9-10 times per 100 meals and McDonald’s in India has more than 320 million customers a year. The entire menu has been customised after extensive market research. Now over 70% of the menu has been changed to vegetarian to cater to customers. Even competitors such as burger king and subway have followed by dropping beef and pork. They have greatly changed the way they plan, make decisions and implement strategies because of the country they are entering.
Ethics
In ethics, CSR comes into play, which every business must do as part of its social responsibility. In India specifically, to remain ethical, McDonalds has begun investing in a eye care hospital, to create an image that is socially responsible, thus making it stand out from its competitors. However there are ethical issues with McDonalds as well. People have been fighting for there working rights due to cases such as wage theft, poor management and bad working conditions. Ethical issues with the food also comes in. There have been cases where McDonalds have given the cows steroids to make more beef. All of these worsen the image of McDonalds.
Globalization
McDonalds is a prime example of globalization. Originating in USA, and slowly expanding into markets and regions where the concept of fast food was not yet discovered. It targeted the middle class segment since it saw a niche, and kept the same interior design, service, and quality of food throughout the world, generating its amazing band image. These things allowed seamless globalisation to take place! Making it one of the largest MNC running today.
Innovation
Innovation is key to remaining competitive. Nearly all the dishes in the menu of McDonalds have been innovated and designed completely by them! Many trends have begun just by McDonalds. These trends aid in creating the brand image of McDonalds, which highly compliment the sales.
Strategy
The company deals with 3 strategic issues.
- How to deal with the growing competition
- How to deal with financial issues such as high franchisee fees in contrast with geographical expansion goals
- How to deal with the worldwide economic crisis
They deal with competition by using aggressive marketing strategies. You will never go a day without noticing a sign that leads you to McDonalds or viewing an ad about it.
Financial issues are dealt with the spreading of risk through globalisation. There are so many franchises that if one goes into loss, there are hundreds of others ready to cover up the loss and make a remarkable profit.
The worldwide economic crisis is something that affects every business, therefore it is not much of a problem for McDonalds as it is already established. It can actually prove to be advantageous as competition is killed off and it is very difficult for new competition to arise. As this affects every business, even the competitors deal with the same struggle, evening out the ‘battlefield’
Starbucks

Change
Due to the continuous changing external and internal factors, change should be managed within businesses if they are to move forward and remain competitive. These factors come from various backgrounds. Those include the population change, culture change, objectives, change and etc. The importance of these factors determines whether the change should take place or not. Sometimes, changes are made, However, not all changes favor the businesses, but also give negative impacts on the business as the changes made do not always guarantee for the business profit. Hence, the businesses should be aware of the surrounding changes in the external environment and need to adapt to the new situation quickly not to be left behind in the business world.
Culture
Although Starbucks is a franchise and has to follow a core menu set by the franchiser, it also has to adjust its products to the country it is located in and its culture. The products it sells has to appeal to the market and their local culture. Since there are many people living in Malaysia who are Muslims, in order for Starbucks to maximise sales it would have to convert into selling Halal products to allow them to attract a wider target audience. By selling Halal products, Starbucks may be one of the few large franchise chains that provide Halal products, allowing them to stand out from competitors. This may increase customer loyalty and sales as consumers repeat their purchases from Starbucks.
The price of Starbucks products would also be influenced by the cultures in the differing countries. Germany is considered a MEDC that is developed and relatively economically stable, compared to parts of Malaysia which may still be seen as developing. Due to Germany’s consistent high quality of life, many people drink coffee and dine at cafes as it has become a lifestyle and social norm. Coffee is seen as a staple in Western culture, and the majority of people in Germany grab a coffee on the way to work. This allows Starbucks to set the prices of its products relatively high as there is a high demand for coffee products. Malaysia on the other hand, has many competing local drinks such as Bubble Tea or Teh Tarik therefore there is a lesser demand for coffee drinks as it is also more commonly seen in Western cultures. Starbucks would be able to break even if they used competitive pricing and priced products at slightly lower than competitors to increase sales. However, Malaysia is becoming more modern and also attracts tourists therefore Starbucks may still survive if their products match competitor’s prices, especially since Starbucks is a well-known and established brand.
Ethics
Starbucks uses cocoa beans obtained only from workers who are paid at least the minimum wage and are not children. They promote this on all of their products to maintain a socially responsible brand image.
Globalization
Starbucks targeted the niche in the market which allowed it to easily globalise and spread its risks. There are downsides with globalization as well, such as different economic situations in different countries, making decision tougher.
Innovation
Innovation is an organizations process for introducing new ideas, workflows, methodologies, services or products due to the sophisticated market demand. It includes researching on possible beneficial product and developing the modern, reasonable, efficient products to gain the competitive advantage over the businesses rivals, contributing the key element in providing aggressive top-line growth. For example, innovation has created new leading industry such as Smartphones. However, sometimes it can turn the business into the great loss. The causes of loss can be from internal or external. From internal, the factors may range from poor time management to poor creativities of the developers. For external, the factors may range from government policies to cultural background depending on the location. So, innovation is the important strategy for the business success.
Strategy
Starbucks has a history of effective marketing strategies. Since McDonalds and Dunkin Donuts entered the coffee industry, there has been an increased competition between them. Starbucks has found more success advertising on a local level rather than to the nation as a whole. The Company advertises a lot through print mediums, as Starbucks’ target market tends to be educated people who do more reading than the average person
Apple

Change
Practically since its inception back on April 1, 1976, Apple has repeatedly captured the world’s attention thanks in large part to its rebellious underdog attitude and continuous efforts to reset expectations of what’s possible from consumer electronics.
Culture
They want every person who joins their team, every customer visiting their stores or calling for support to feel welcome. They believe in equality for everyone, regardless of race, age, gender, gender identity, ethnicity, religion, or sexual orientation. That applies throughout their company, around the world with no exceptions. Recently apple added new racial emoji’s consisting of faces with different colour’s to apple to the races in the world.
Ethics
Around the globe, Apple employees are united in bringing equality, human rights, and respect for the environment to the deepest layers of our supply chain. They demand that suppliers treat workers fairly and ethically at all times.
Globalization
First of July 2013, Apple has developed 417 retail stores in 13 countries and an online store available in 38 countries with global sales of $16billion dollars in merchandise in 2011. As a multi-national corporation, Apple Inc has realized the significance of globalization by spreading all over the world.
Innovation
Apple has always been different as they have had a different perspective of the world, they aspire to do more things and to have the opportunity to create the best products in earth, products that change lives and help shape the future.
What is Apple’s fundamental soul? The company’s motto, “Think Different,” provides a hint. Apple maintain an introspective, self-contained operating style that is capable of confounding competitors and shaking up entire industries
Strategy
- Apple Brand Personality
- Customer Experience
- Apple Brand Architecture
- Apple Halo Effect
- Corporate Market
- Apple Watch
- Original Mac Marketing Strategy
References
- https://www.scribd.com/document/577122644/CUEGIS-EXAMPLES-McD-STARBUCKS
- https://www.ibid.com.au/products/business-management-4th-edition
- https://dp.uwcea.org/docs/Business%20Management%20Subject%20Guide.pdf
- https://thinkib.net/businessmanagement/page/21720/the-cuegis-essay



