Table of Contents
- STEEPLE Analysis
- PESTLE Analysis
- How Changes in STEEPLE Factors Affect A Business’s Objective & Strategy
- Simple Review Questions
- Past Paper Review Questions
- Command Terms
- References
- Click Here To Learn More About Unit 1.7!
STEEPLE Analysis
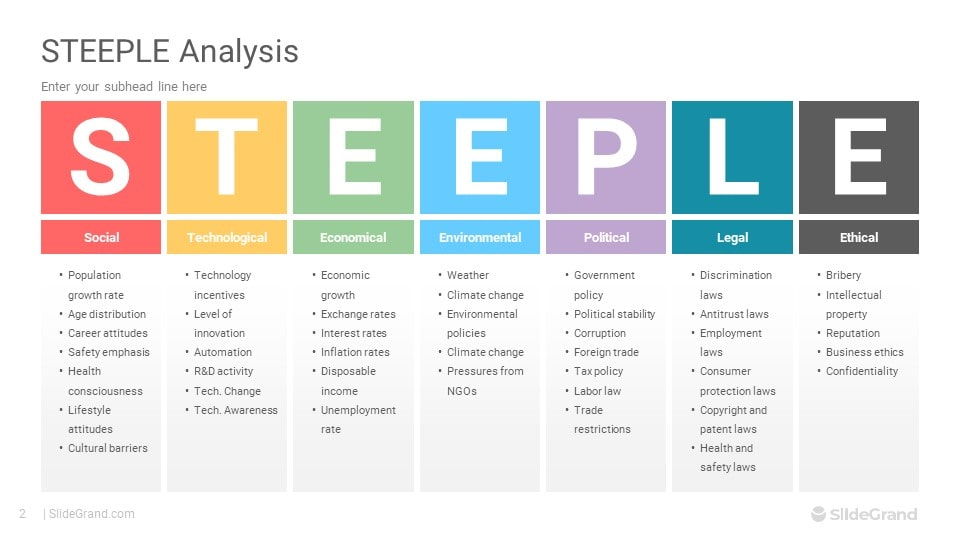
Definition
It is an analytical framework used to examine the opportunities and threats of the external environment (social, technological, economic, environmental, political, legal, and ethical environments) on business activity.
Sociocultural Factors
Factors that span societal norms, cultures, and demographics. They invariably shape consumer attitudes, behaviors, and expectations.
1. Growing support for environmental protection
Many organizations are now aiming to apply environmentally sustainable business practices, and report the non-financial aspects of their operations, for instance, recycling and waste management.
2. Liberal and modern social attitude towards women
A more flexible attitude towards women would increase the number of people in the workforce, and improve the business’ productivity as most women often have a creative instinct when coming up with innovations or how to improve organizational culture in a business. With a more liberal and modern social attitude towards business, they will benefit from a more flexible labor force, due to higher demand for female workers. This may also improve the business’ overall productivity and maintain its competitive advantage.
3. Migration and the increased acceptance of multiculturalism has created more choices for consumers
The introduction of new cultures from immigrants from around the world would bring increased variety of goods and services within that country. For example, the most consumed take-out food in the UK is Indian curry, whilst Finland is the largest non-Asian importer of Malaysian laksa/spicy noodle soup. The increased effects from migration may also improve worker recruitment since there are higher availability of migrants who are part of the labor force.
4. Societal pressures on businesses to act ethically and socially responsibly
Governments and pressure groups demanding businesses to act ethically and socially responsibly would encourage businesses to maintain CSR (Corporate Social Responsibility) as a way to preserve a positive brand image and maintain their customer loyalty. Businesses are often encouraged to practice environmentally sustainable processes such as recycling used materials and making use of biodegradable resources to produce products, so that they do not increase waste pollution and improve the well-being of the environment.
5. Demographic changes in society, for instance, a higher ageing population
Ageing population in economically developed countries have affected recruitment practices, marketing strategies and the products supplied by businesses. Often, women are opted to have children at a later age as they give their careers priority, providing further opportunities for businesses. Changing trends regarding consumption habits/fashion sense or rates of birth and mortality, may influence the demand for the products consumed or services since the population trends which are connected with customer base.
6. Language presents a barrier for multinational companies are aware
Language plays a crucial role in business, presenting both opportunities and threats. Effective communication across different languages and cultures can enable market expansion, enhance customer relations, and provide a competitive edge. However, poor translations and cultural misunderstandings can harm brand image and lead to legal issues. To navigate these challenges, businesses should prioritize localization over direct translation, invest in professional translation services, provide cultural training for employees, and collaborate with local experts. By adopting these strategies, businesses can turn linguistic and cultural differences into opportunities for growth and success.
Technological Factors
Technological factors spotlight the impact of technological advancements and innovations on the operational context and competitive environment of businesses. This can be in forms such as:
- new working practices
- increased productivity and efficiency gains
- quicker product development time
- job creation
- new products and markets
Economic Factors
Factors that include economic growth, exchange rates, and inflation rate which carry direct and indirect impacts on businesses’ cost structures, pricing strategies, and market demand. The examples vary such as:
- Climate change = this poses a threat to businesses as they can risk the supply of raw materials due to changes in weather
- Inflation = the higher the inflation, the higher the risk of the company’s purchasing power to become eroded, while increasing production costs and putting pressure on its profits and margins
- Interest rates = they affect financing costs such as loans and credit lines used to finance its operations or expansion plans. It also makes it more expensive for businesses to sell the
- Exchange rates = the rates of currency that are employed between two countries can affect the prices of imports/exports
- Taxation policies = taxes will affect the business operations and increase its production costs
- Economic growth = the increase in a country’s economic activity over time and is measured by the change in the value of the economy’s total output (aka. GDP/Gross Domestic Product)
- Unemployment rate = the proportion of a workforce not in official employment; level of skilled and non-skilled workers in a country (quality and quantity of labour)
Environmental Factors
Factors that affect the natural environment. Many businesses rely on the natural environment for inputs, and changes in the natural environment can have a large impact on the business.
Changes in social attitudes towards the environment have meant that the business are increasingly reviewing their practices. Firms that do not respect the environment face ruining their reputation and long-term profits. The weather and seasonal changes can either present opportunities or threats for the business, some may choose to exploit from the profits such as tourism activities, tour operators focusing on ski holidays in the winter and beach resorts in the summer.
Political Factors
Factors which reflect the legal framework of the country the business operates in. It embodies the influence of government actions and political stability on business operations.
These policies are fiscal and monetary policies, and can be in two forms, either expansionary or contractionary. Fiscal policy means the use of taxation and government expenditure policies to influence business activity. Monetary policy means the use of interest rates/exchange rates to raise either the aggregate demand or aggregate supply of a country.
Deregulation can also be used to increase competitiveness of a firm due to the removal of government policies and regulations which constrain business activity within a particular industry.
However, corruption levels can be a major and ongoing threat for a business, as it can jeopardise the nation’s ability to alleviate poverty/standards of living. To be competitive in an industry, it is more beneficial if the levels are lowered.
Legal Factors
Factors or legal standards that business must meet and consider to help reduce any adverse effects from a company’s operations, corporate image and profits.
1. Consumer Protection Legislation
Laws that make it illegal for businesses to provide false or misleading descriptions of their products and services. Products must meet certain quality standards and be fit for their purpose. Businesses are held liable for any damage or injury caused by their defective products.
2. Employee Protection Legislation
Regulations that protect the interest and safety of workers. For example:
- Anti-discrimination laws help ensure that business act fairly towards their employees irrespective of their age, gender, religion or ethnicity.
3. Competition Legislation
Laws ensure that anti competitive practices are prohibited to protect customers and smaller businesses from firms with monopoly power. The government takes action against firms that are large and act against public interest. For example: firms that engage in price fixing or charge extremely high prices.
Competition laws can also present opportunities, for example:
- Copyright, trademark and patent laws give business legal protection against competitors replicating their works or inventions, stimulating innovation and improving firm’s competitiveness.
4. Social and Environmental Legislation
Regulations that exist to prevent or reduce the consumption of demerit goods. For example:
- tobacco
- petrol
- alcohol
- gambling
- illegal drugs
The external social costs of consuming demerit goods outweigh the private costs of consumption. With government legislation, the consumption of these products would be lower and therefore the costs to society would be lower. For example:
- passive smoking
- pollution
- crime rates
Ethical Factors
Factors which reflect the moral principles of a business that ought to be considered in the decision-making process.
Ethical firms acting in socially responsible way towards their stakeholders e.g. protecting the natural environment by using resources effectively and minimizing waste. These firms will pay their workers on time and do not employ workers below the legal minimum age/allow their employees to operate in poor working conditions.
Firstly, they attract and retain good quality workers.
Second, they can attract new customers and retain existing ones. To remain competitive, businesses need to consider the impact of their operations on society and the environment because the customers are increasingly concerned about environmental protection and ethical business behavior.
Lastly, staying socially responsible can help generate good publicity and public relations. These can be helped by recording/conducting social audits regarding performance levels of community projects and level of pollution caused by firms’ operations. The business might not be able to pursue the cheapest/profitable option due to costs of being ethically and socially responsible, such as suppliers, because they are deemed as unethical.
Summary
| Social Factors | – Changes in demographics, in lifestyle – Social mobility – Trends, fashion, tastes – Education |
| Technological Factors | – New technologies, new discoveries and inventions – IT, e-commerce – Research and Development (R&D) |
| Economic Factors | – Economic growth or recession – Employment, unemployment, inflation, interest rates – Exchange rates between currencies – Climate change – Taxation policies |
| Environmental Factors | – Changes of value in society – Increase in CSR and fair trade practices, codes of business behavior – Corruption, anti-corruption |
| Political Factors | – Elections resulting in changes to government policies and priorities – Political stability or instability – Lobbying (communicating with any official in the legislative or executive branch for the purpose of attempting to influence legislative or administrative action or a ballot issue) |
| Legal Factors | – Changes in legislation that may affect employment, consumers, production, health and safety etc – Competition laws between countries or blocs of countries |
| Ethical Factors | – Climate change, global warming – Pollution – Depletion of non-renewable resource |
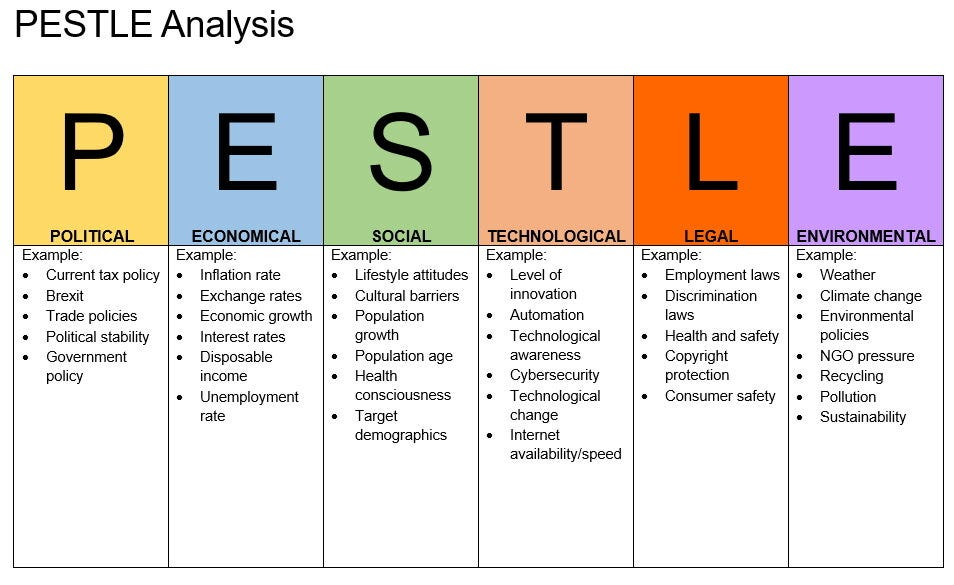
PESTLE Analysis
It is similar to STEEPLE, which analyzes the business’ macro environment for external factors (political, economical, social, technological, legal, environmental) that have significant impacts on operations, decision-making, and future strategies. The same range of factors can be applied in this analysis, except it is shorter to carry out.
How Changes in STEEPLE Factors Affect A Business’s Objective & Strategy
- Changes in trends, social norms, public view on ethics can affect the company’s products, business activities, and the way they market their products
- Changes in legal or political factors can force businesses to change the way they operate to comply with new laws or regulations
- Changes in technological factors can result to the company adopting newer technology or automation processes to increase efficiency or keep up with industry standards
- Changes in environmental factors could force companies to adapt to scarce raw materials, frequent natural disasters, etc.
- Changes in economic factors (economic growth, interest rates, etc.) could affect the costs of operations of the business, spending attitude of consumers, etc.
Simple Review Questions
- What does STEEPLE stand for?
- What are the stages of business cycle
- Distinguish between strengths and weaknesses!
- Differentiate between opportunities and threats!
- State few examples for sociocultural factors and technological factors!
- List down several examples for economic and environmental factors!
- Differentiate between environmental and political factors!
- Explain the various stages of business cycle.
- What differentiates between a recession and a boom.
- State the opportunities and threats of having internet technologies.
Past Paper Review Questions
Question 1

Answer
| Business Decisions | Internal constraints | External constraints | |
| (A) | Kraft Food announces takeover of Cadburry | – High costs from takeover – Meshing up of organizational culture can lead to disruptions and conflict in | – Local community may be against the – Cadbury may also suffer from |
| (B) | Singapore Airlines plans to move call centre into India | – Singapore Airlines may have to renew their labour force and retrain their workers to adjust with the language barriers in India – Singapore Airlines may also need to purchase new facilities in India to – Singapore Airlines | – Singapore Airlines may also need to – Singapore Airlines |
| (C) | Disney set to open new theme park in Shanghai | – Internal funds, e.g. a lack of retained profits to finance the expansion plans – Resistance from senior staff to relocate to China – Lack of marketing knowledge to cater for a foreign (Chinese) target market – Inaccurate or imprecise marketing research data | – A lack of cultural awareness (diversity) – Language and communication problems – Unfamiliarity with Chinese legislation, including employment laws – Less affluent people, in general, in China compared to USA or Europe – Existing competition from well-established theme parks in Shanghai |
| (D) | Virgin Atlantic unveils plans to start daily flights to Nairobi, Kenya |
Question 2

Answer
| Demographic changes | Opportunities | Threats | |
| (A) | Growing number of self-employed people | – Consultation, advisory and supply chain opportunities – Financial service providers are likely to benefit from patronage, e.g. banks and insurance firms | – Smaller pool of potential employees/recruits i.e. labour shortages, thus leading to higher wages having to be paid – Possibly an increase in competition from those who have set up their own businesses |
| (B) | An increasing number of single-parent families | – Prospects for child care and related products – Impact on workforce planning, e.g. labour flexibility | – Labour immobility – Relatively low income earners (or low disposable incomes) – Possible reduction in size of potential labour force |
| (C) | Adults choosing to have fewer children and at a later stage in their lives | – Career development of female workers – More females opting for full-time employment – Perhaps a greater labour supply in the short term – Higher disposable income | – Long term impacts on related industries, e.g. school and toy manufacturers – Smaller workforce in the future |
| (D) | An increasing number of people graduate with university degrees | – Increasing potential pool of skilled and qualified workers – Increased productivity – Higher earners lead to greater spending in the economy | – Higher salaries as firms compete to attract the best workers – Reduced workforce as more people enter higher education (postponed entry to the workforce) – Possibly higher staff turnover as skilled employees tend to be more mobile/headhunted |
Question 3

Answer
(a) Market segment refers to a distinct consumer group or part of the market for a particular product, e.g. children, women, adults, teenagers, the elderly or high income earners.
(b) The technological environment can present a range of opportunities for hi-tech firms (such as Nintendo and Apple), which include:
- The ability to produce more sophisticated consoles, games and other gadgets (such as the iPod) to appeal to a larger and wider market
- Quicker product development times; essentially in fast-paced industries where products may have a short product life cycle
- Marketing opportunities are enhanced with the use of improved technology, e.g. purchasing music online through iTunes
- Any other relevant factor that is explained in context.
Question 4

Answer
(a) Factors that could have caused inflation in Zimbabwe:
- Cost-push inflation , e.g. caused by soaring fuel and food prices.
- Demand-pull inflation, e.g. Zimbabwean citizens getting large pay rises (due to the increasing cost of living), thereby fueling even higher prices.
- The Zimbabwean government printing more money, thus raising the money supply and reducing the value of its money.
(b) Uncontrollable inflation can affect businesses in Zimbabwe in several ways, including:
- Reduces the international competitiveness of the economy – this will make it more difficult for Zimbabwean businesses to sell their exports, thereby hindering their success.
- The level of national output is likely to decline due to soaring costs of production; this will have detrimental effects on businesses in the country.
- Investment (including foreign direct investment) is likely to decline as business confidence falls. This hampers future business activity in Zimbabwe.
- Standards of living are likely to fall, causing further social and economic problems for the poverty- ridden country, again negatively affecting businesses.
Question 5
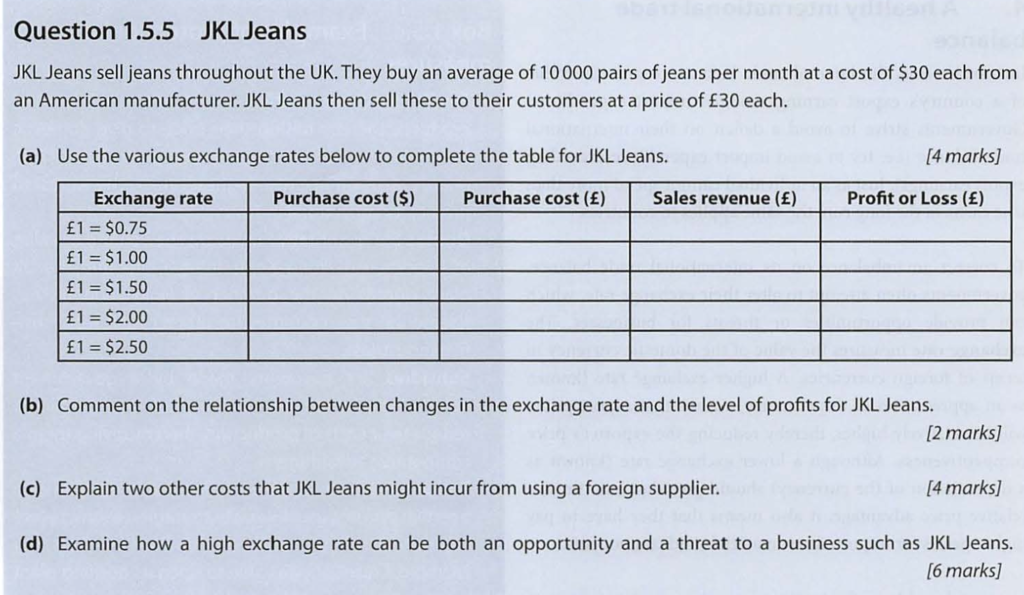
Answer
(a)
| Exchange rate | Purchase cost ($) | Purchase costs (£) | Sales revenue (£) | Profit or Loss (£) |
| £1 = $0.75 | 300 000 | 400 000 | 300 000 | (100 000) |
| £1 = $1.00 | 300 000 | 300 000 | 300 000 | 0 |
| £1 = $1.50 | 300 000 | 200 000 | 300 000 | 100 000 |
| £1 = $2.00 | 300 000 | 150 000 | 300 000 | 150 000 |
| £1 = $2.50 | 300 000 | 120 000 | 300 000 | 180 000 |
(b) There is a positive relationship between the exchange rate and the level of profits for JKL Jeans. For example, when the exchange rate (for pounds sterling) rises from $1 to $2, the profit rises from zero (break-even) to £150 000 because JKL Jeans is able to purchase from its US supplier at a lower rate.
(c) Costs of engaging in international trade include:
- Tariffs imposed on the import of American jeans
- Transportation costs for the jeans being shipped in from the USA
- Insurance for the stock being transported from overseas.
(d) A high exchange can create an opportunity for JKL Jeans because the costs of importing its stocks of jeans will fall. As the £ strengthens against the $, JKL Jeans will be able to purchase the same quantity of stock for a lower cost, e.g. as the £ strengthens from $1 to $2, the purchase costs in terms of sterling will halve. This means that the profit margins of JKL Jeans should increase.
However, a stronger currency can also present threats if the business exports its products. A stronger currency means that the price of jeans sold by JKL Jeans overseas will automatically increase. This makes its exports less price competitive (through no fault of its own).
Question 6

Answer
(a) The term ‘brand’ refers to the use of an exclusive name, symbol or design to identify a specific product or organization, such as ‘Amoy’. It is used to differentiate a product from similar ones offered by rival firms.
(b) Unethical behaviour is not necessarily illegal, although it is often difficult to separate the two. Amoy Food acted unethically by misleading customers into believing that its products were free from MSG, i.e. by making false advertising claims. However, some might argue that the traces of MSG found in Amoy Food’s products were not deliberate; although this could raise issues about quality assurance. Amoy Food also acted illegally because of the potential health issues arising from its wrongdoing, given that Hong Kong enforces laws against the false labelling and advertisement of food products.
Question 7

Answer
(a) Discrimination refers to the negative prejudice against, or intolerance with, a particular trait. Examples include discriminating against people because of their race, religion, sexual orientation, physical appearance or gender (as in the case of Walmart).
National minimum wage refers to the legal requirement for all employers, such as Walmart, to pay their workers at least the amount stipulated by the law, e.g. $7.25 per hour.
(b) It is important to observe and adhere to labour laws such as rest breaks. Not only does this directly affect the productivity of the workforce, there will also be a knock-on effect on staff morale if sufficient breaks (a hygiene factor) are not given. As a minimum compensation, workers who are asked to work overtime, perhaps during their usual rest breaks, should be paid a premium rate. In the case of Walmart, the discriminatory employment practices led to lawsuits that amounted to $78 million.
The case study also points out the importance of adhering to equal opportunities legislation, i.e. paying men and women the same rate of pay for equal work. Male workers should not be offered promotion over women simply because of their gender. If a woman is better suited for the job, then it makes business sense to offer the position to her. Not only is this fair but it also suggests that business-decision making is more rational.
Finally, with all the negative publicity it is likely that the corporate image of Walmart, both as an employer and as a retailer, would have been somewhat damaged.
Despite the potential to save money by ‘cutting corners’ (i.e. not complying with labour laws), in the long run the financial penalties and detrimental impacts on the organization mean that it is perhaps best for large companies such as Walmart to be aware of and comply with the legal environment.
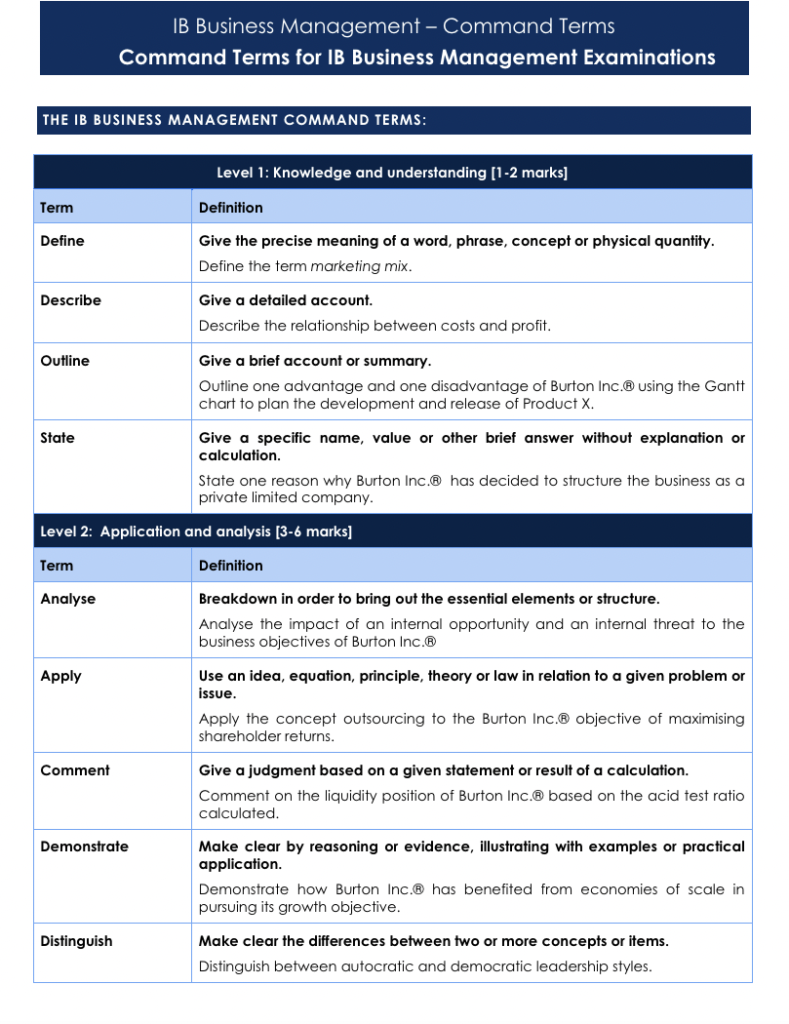
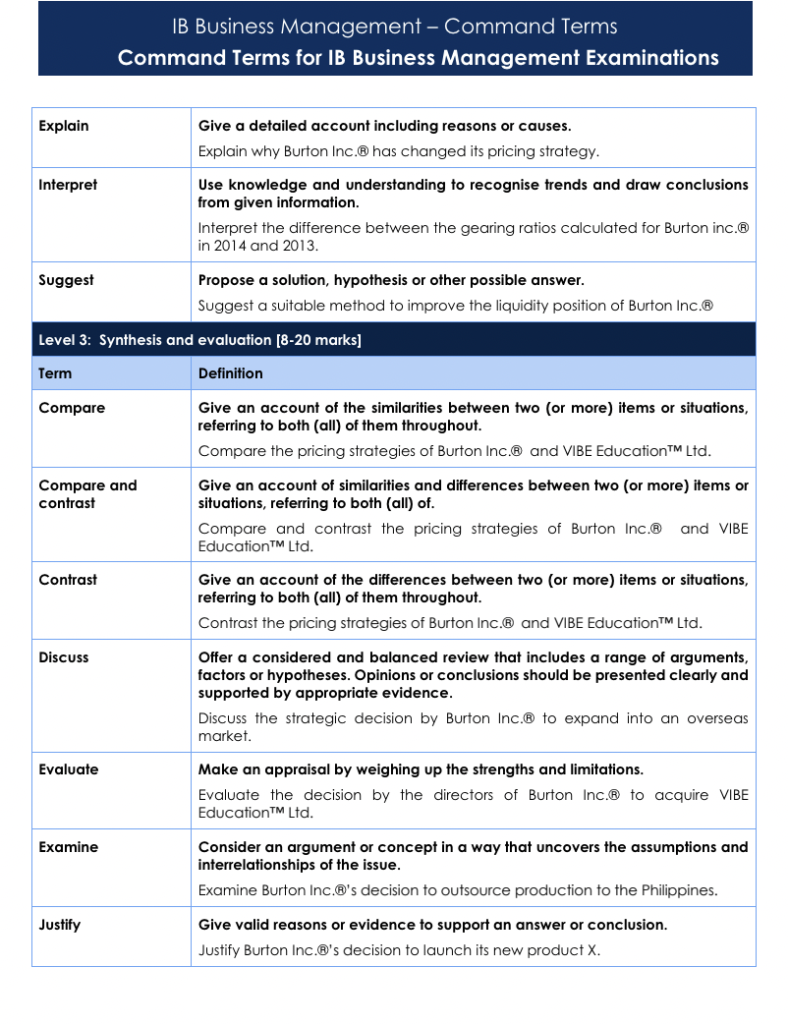
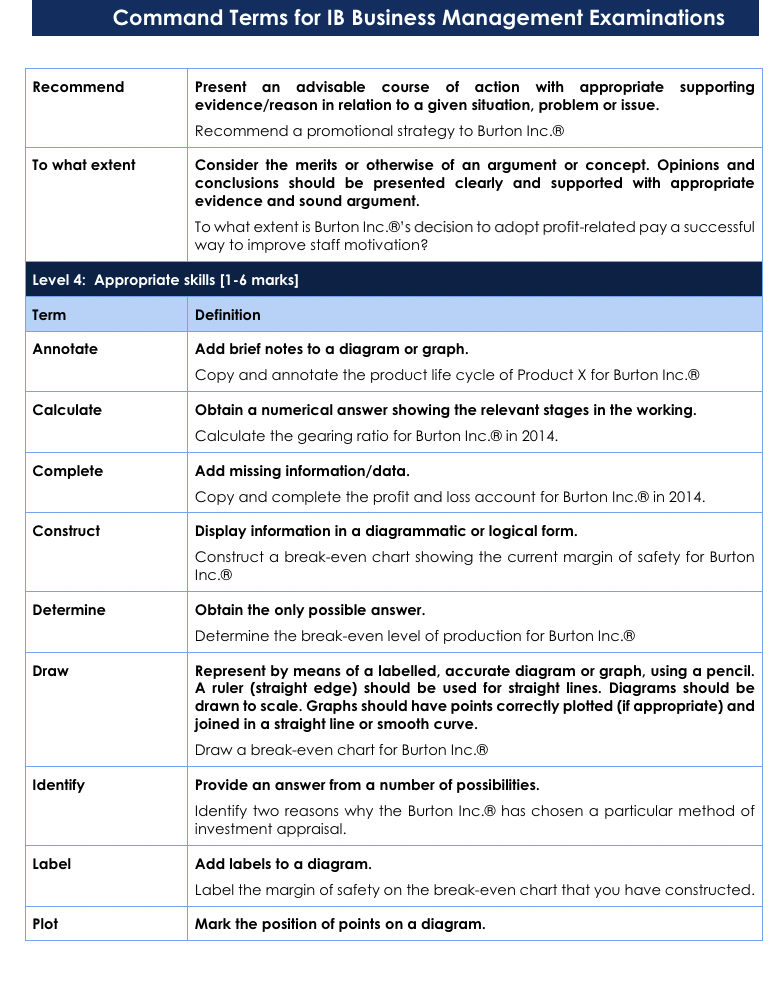
Command Terms
References
- https://ebooks.papacambridge.com/viewer/ib/group-3-individuals-and-societiesbusiness-management-ibid-business-management-paul-hoang-third-edition-ibid-2014-pdf
- https://www.tutorchase.com/notes/ib/business-management/1-5-2-pestle-analysis
- https://www.businessmadeeasy.xyz/business-basics/1-5-external-environment/



