Table of Contents
- Aims, Objectives, Strategies, and Tactics
- Tactical Objectives vs. Strategic Objectives
- SMART Objectives
- Mission vs. Vision
- The Need For Changing Objectives
- Ethical Objectives
- Advantages & Disadvantages of Ethical Behavior
- How To Maintain Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
- SWOT Analysis
- Ansoff Matrix
- Simple Review Questions
- Past Paper Review Questions
- Command Terms
- References
- Click Here To See Unit 1.5!
Aims, Objectives, Strategies, and Tactics
| Aims | – General and long-term goals of an organization – Broadly expressed as vague and unquantifiable statements – Set by senior directors of organization – Qualitative nature – e.g. provide education for all |
| Objectives | – Short-to-medium term – More specific and quantifiable – e.g. achieve a 95% pass rate with two years – Encourage to use of ICT to enhance teaching and learning – Important for 3 reasons: 1) measure and control: a firm’s plans as they set the boundaries for business activity 2) Motivate: help inspire managers and employees to reach a common goal 3) Direct: provide an agreed clear focus for all individuals and departments of an organization |
| Strategies | – Plans of action to achieve the strategic objectives of an organization – Outlines the direction in which the business wants to make and resources it will give to attain competitive benefits – e.g. cost leadership, differentiation, focus on marketing products to niche markets – Types of business strategies: 1) Operational strategies = day-to-day methods; reach tactical objectives 2) Generic strategies = those that can affect the business as a whole; competitive advantage 3) Corporate strategies = long term aim of the business; strategic objectives |
| Tactics | – Short-term methods used to achieve an organization’s tactical objectives – Specific actions taken to implement the initiatives outlined in the strategy – e.g. putting your brand on magazines/billboards |
Tactical Objectives vs. Strategic Objectives
| Tactical Objectives | Explanation | Strategic Objectives | Explanation |
| Survival | – Start ups are vulnerable to encounter problems such as limited recognition from customers/intense competition from rival firms – Risk of being a takeover target | Profit maximization | – Maximize profits; an incentive for businesses to set up and run – Attract investors (through dividends) |
| Sales revenue maximization | – Strive to maximize sales revenue to establish themselves in the market place – Sales are linked to earnings – e.g. selling insurance and relying on sales agents to distribute | Growth | – Measured through the increase in sales revenue/market share – Failure to grow can lead to declining competitiveness |
| Market standing | – A business has a presence in industry – Due to innovative products and designs, being socially responsible or largest market retailer | ||
| Image & Reputation | – Portrayed by media – Ways to achieve this: improved customer level, better facilities, after sales-care |
SMART Objectives
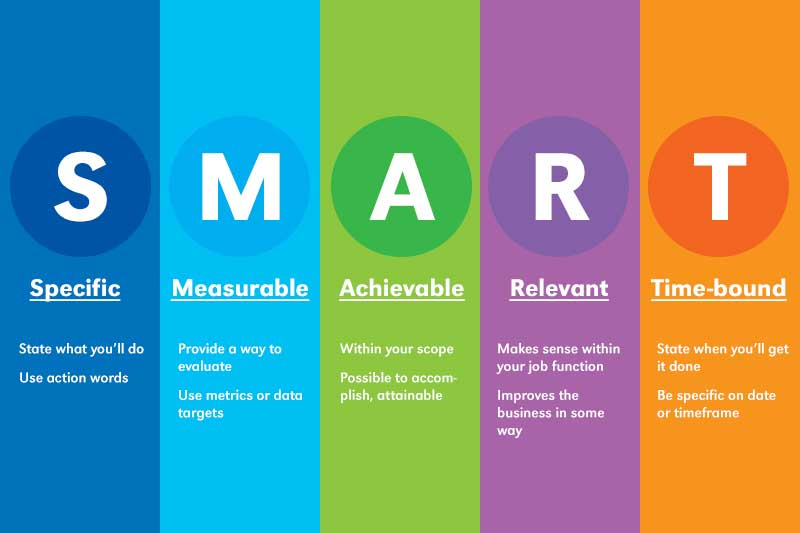
| Specific | Objectives need to be precise/defined |
| Measurable | Objectives should be quantifiable targets |
| Achievable | Objectives must be practically feasible (attainable) |
| Realistic | Objectives are reasonable given their limited resources |
| Time constrained | Objectives should be achieved within a specified time period/measurements |
Mission vs. Vision
| Mission | – Specific to what the business wishes to achieve – Outline values of the business – Beliefs and guiding principles that set the framework of the organization – Operate a daily basis – Updated more frequently – e.g. “what is our business?” |
| Vision | – Purpose of setting mission statements – Updated not so often – e.g. “what do we want to become?”, “” |
The Need For Changing Objectives
Internal Factors
| Corporate culture | – More flexible and adaptable organizational culture – Have innovational objectives |
| Type and size of organization | – Legal structure of a business is likely to cause a change in its objectives – Separation of ownership and control, various stakeholder objectives need to be considered included managerial objectives and shareholder objectives |
| Private vs. public sector organizations | – Private sector firms are mostly focused on profit maximization – Public sector organizations provide a service |
| Age of the organization | – New firms tend to have short-term objectives: break even and survival – Established firms strive for long-term objectives: growth and higher market share |
| Finance | Amount of available finance will determine the scale of firm’s objective |
| Risk profile | If managers and owners have relatively high willingness and ability to take risks |
| Crisis management | – Face internal crises such as unexpectedly high rates of self-absenteeism and staff turnover, falling productivity, and motivation problems, liquidity problems, quality standards |
External Factors
| State of the Economy | – Booms provide opportunities for new businesses – Slumps cause threats for business |
| Government Constraints | – Regulations – Environmental protection laws |
| Presence and Power of Pressure Groups | – Force a business to review its approach to ethics through lobbying – Harm a firm’s image if it is not adopting socially responsible approaches |
| New Technologies | – New business opportunities – Use of e-commerce – Digital technologies |
Ethical Objectives

Ethics
Ethics are moral principles that guide decision making and strategy. Morals are concerned with what is considered to right or wrong, from society’s point of view.
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
The conscientious consideration of ethical and environmental practices related to business activity. A business that adopts CSR acts morally towards its various stakeholder groups and the wellbeing of society as a whole.
Code of Practice
The number of businesses aiming to achieve ethical objectives have decided to implement code of practice, and publish it in their annual report. This refers to the documented beliefs and philosophies of an organization.
Views & Attitudes Towards Businesses Achieving Ethical Objectives
| Self interest attitude | – To generate profits for their owners/shareholders/ – By being profit-motivated, the business is able to be more efficient and prosperous which indirectly helps society through job creation, wealth creation and corporate tax payments |
| Altruistic attitude | – Humanitarian and unselfish behavior – Do what is possible to improve society – Willingly donate money to charity/investing in local community projects regardless of whether their actions can increase profit |
| Strategic attitude | – Business have to be socially responsible only if it brings profit – e.g. CSR as a method of long-term growth |
Advantages & Disadvantages of Ethical Behavior
| Advantages | Explanation | Disadvantages | Explanation |
| Improved corporate image | – Acting socially responsible help to enhance corporate image and business reputation – Media and pressure groups can place pressure on organizations to act responsibly | Compliance costs | – Costs of socially responsible behavior are very high – More expensive to harvest than genetically modified crops due to the additional time and money involved |
| Increased customer loyalty | – Loyalty will increase if a business acts morally – e.g. ethical policy of not testing the products on animals | Lower profits | – Profitability is likely to fall – Business exists when ethical decision-making involves adopting a less profitable course |
| Cost cutting | – Being environmentally friendly can reduce the amount of of packaging – Benefit from avoiding litigation costs due to unethical and irresponsible business activities | Stakeholder conflict | – Not all stakeholders are keen on the business adopting CSR, especially if this conflicts with other objectives – Speculative shareholders and financial investors – Managers may be pursued into pursuing goals other than ethical ones |
| Improved staff morale and motivation | – Ethical and socially responsible behavior can help businesses attract and retain highly motivated staff | Ethics & CSR are subjective | – Views about what is considered principles held by invisible – Legislation help to provide guidelines about what is socially acceptable |
How To Maintain Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)
| Provide accurate information and labelling | – Can help consumers to make better informed decisions – e.g. truthful nutritional information |
| Adhering to fair employment practices | – Providing decent working conditions – Fair remuneration – Training opportunities |
| Having consideration for the environment | – Seek to use more recycled materials in the production process, recycle a greater proportion of waste – Aim to reduce pollution caused by their operations |
| Active community work | – Voluntary and charity work – e.g. sponsoring and participating in local community events |
SWOT Analysis
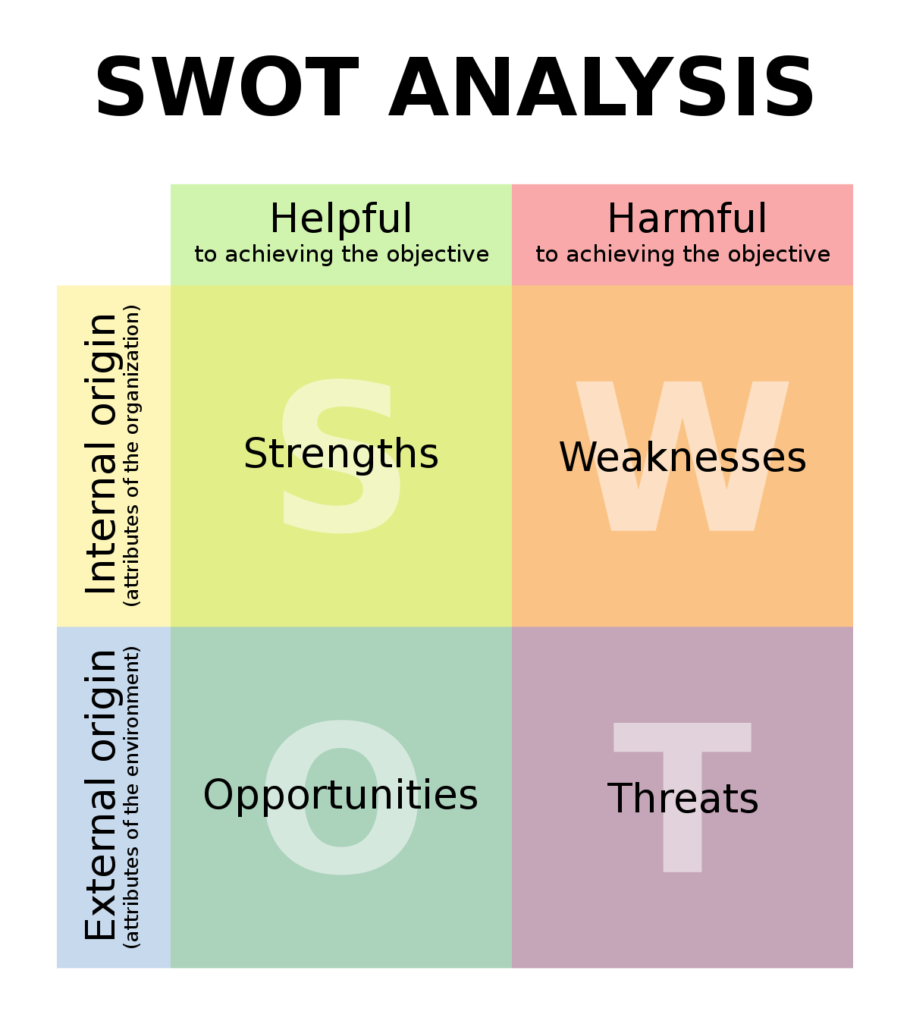
Definition
SWOT Analysis is a simple yet very useful and analytical tool used to access the internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats of a business decision, issue or problem. It can be used for the following:
| Functions | Example |
| Competitor analysis | – Threats posed by a rival – Strengths of a competitor |
| Assessing opportunities | – Development and growth of organization |
| Risk assessment | – Probable effects of investing in a certain project/location |
| Reviewing corporate strategy | – Market position – Direction of the business |
| Strategic planning | – Decision to diversify/expand overseas |
Standard Format
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
| – Unique selling point – Brand awareness and brand loyalty – Experience, knowledge, skills – Corporate image and reputation – Accreditation | – Limited sources of revenue – Escalating production costs – Poor cashflow – Poor location – Higher competitor prices |
| Opportunities | Threats |
| – Economic growth – Trade liberalization – Weakening exchange rate – Demographic social lifestyle changes – Mergers and acquisitions of firms | – Economic downturn (recession) – Inflation – Outbreak of infectious diseases – New competitive entrants – Negative media coverage |
Advantages & Disadvantages of SWOT Analysis
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Wide a range of application | Rather simplistic/does not demand detailed analysis |
| Helps determine the organization’s position in the market + formulation of business strategy for its survival | Model is static whereas the business environment is always changing |
| Allows foresight and proactive thinking in the decision making process | Open about the weaknesses and willing to act upon them |
| Reduce the risks of decision making by demanding objective and logical thought processes | Not typically used in isolation |
Ansoff Matrix
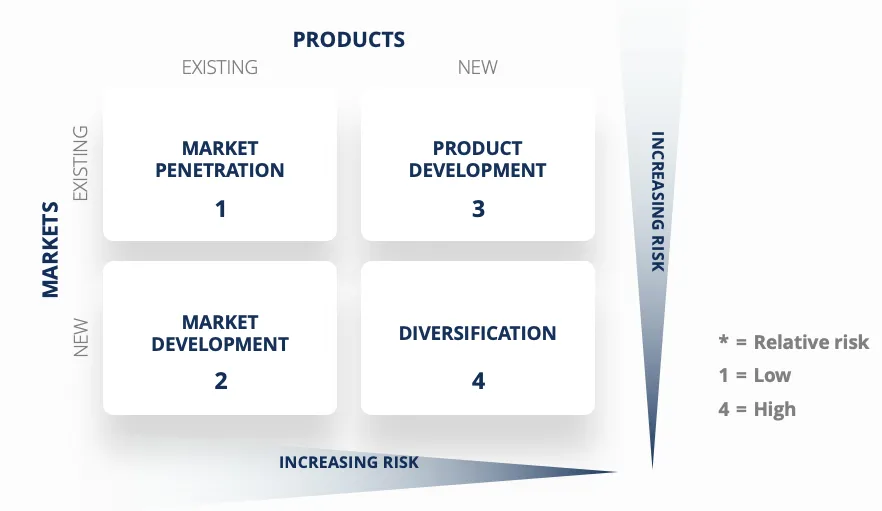
| Market Penetration | Product Development | Market Development | Diversification |
| Same products for existing market | New products for existing market | New market for existing products | New products for new market |
| Minimal risk | Moderate risk | Moderate risk | High risk |
| Seek to maintain/increase market share | Innovation to replace existing products | Entering overseas markets | Spreading risks |
| Intense competition | Product improvements | New distribution channels | Use of subsidiaries & strategic business units |
| Improve advertising, enhancing product qualities | Brand development (through advertising, research & development) | Different pricing policies | Exploit brand name, employ different technologies, implement new qualities to the product Risk of not being successful in one strand may not harm the business entirely |
Simple Review Questions
- Differentiate between vision and mission statements!
- Distinguish between strategic and tactical objectives.
- Define ethical objectives and CSR, then state its types!
- State 2 advantages and disadvantages of CSR.
- What does it mean to have SMART objectives for a business?
- Explain the use of SWOT Analysis!
- Explain about Ansoff Matrix!
- State any 3 reasons why a business needs to change its objectives (internal and external factors)!
- What is the difference between market penetration and market development?
- State the way to maintain CSR?
Past Paper Review Questions
Question 1

Answer
(a) ‘Mission statement’ refers to the declaration of an organization’s overall purpose, such as Walt Disney Company’s ‘To make people happy’. It forms the foundation for setting the objectives of a business.
(b) The role of vision and mission statements in a business organization includes:
- to have a clear purpose, i.e. what the business is trying to achieve
- outlines the organization’s values
- states the underlying purpose of an organization’s existence
- serve to unify all people and corporate cultures within the workforce
Question 2

Answer
(a) Strategy can be defined as the long-term plan of a business in order to reach its organization aims. It gives the organization sense of direction and scope to achieve competitive advantages over the long term. Market share is a measure of the power that a business has within its industry and is usually measured by calculating the firm’s sales revenue as a percentage of the industry’s sales revenue.
(b)It is important for Lenovo to specify its organizational objectives for several reasons, including:
- To provide focus and a sense of purpose for its staff
- To measure the performance of the business
- To inform strategic planning and decision-making
- Credit any other valid point written in the context of Lenovo
(c) Reasons (barriers) that might prevent Lenovo from meeting its objectives include:
- Conflict, e.g. ‘Trust and integrity’ might place some limits on Lenovo’s ability to earn high profits. Alternatively, shareholders might demand high dividends, but management seek to invest profits for the long term.
- Culture clash, e.g. compatibility of Chinese and American cultures, despite Lenovo’s commitment to ‘Teamwork across cultures’.
- Financial constraints, e.g. sponsorship commitments could harm Lenovo’s cash outflow in the short term; any benefits are only reaped in the long run.
- Any other valid reason that is examined in sufficient detail and written in the context of Lenovo
Question 3

Answer
(a) Ethical business behaviour means that McDonald’s and Burger King operate in a moral (principled) manner, rather than acting purely for commercial gains. Ethical actions, such as improving the wellbeing of children or using humanely sourced meat, would be considered as being ethical and socially responsible behavior.
(b) Whether acting ethically can provide McDonald’s and Burger King with commercial and competitive advantages will depend on the relative strengths of taking such actions.
- Potential advantages of such behaviour include
- Easier to recruit staff and improved staff retention as employees feel that they work for a socially responsible employer
- Greater employee satisfaction, morale and motivation, which helps to boost productivity and reduce labour turnover
- Improved corporate and brand image; particularly important as the image of fast-food chains have been tarnished by health concerns such as child obesity
- Ethical behaviour is a way of differentiating products and services from rival firms, thereby possibly taking market share from competitors and/or encouraging customer loyalty.
- Local communities are more likely to welcome the fast food companies and pressure groups are less likely to oppose them.
- Ultimately, these factors can, in the long run, lead to improvements in the competitiveness, sales and profits for McDonald’s and Burger King.
However, the potential drawbacks of introducing ethical and socially responsible activities include:
- Compliance costs mean that there are additional expenses to both companies, e.g. McDonald’s donating funds to help ill children and their families and Burger King having to source their suppliers.
- Higher costs mean that profits margins will fall, unless prices are increased (which is perhaps unlikely in highly competitive markets such as fast food where price is a fundamental deciding factor).
- Since Burger King has also decided to act in an ethical way, albeit by alternative actions, McDonald’s might lose any initial competitive advantage that it might have had (but the higher costs remain).
- It is not known whether consumers genuinely care about a firm’s ethical policies – what is more important to diners: price and taste of the food or whether the restaurants donate money to charitable organizations?
- Ultimately, these factors are likely to increase the costs to McDonald’s and Burger King, thereby possibly leading to lower profit margins for both firms.
- Some stakeholders, such as shareholders, may therefore oppose these activities if they believe that there will be reduced profits overall.
Question 4

Answer
(a) Possible barriers to socially responsible business behavior might include:
- Compliance costs, i.e. the costs of implementing ethical and socially responsible practices
- Management ignorance, i.e. there is limited awareness of the issues, costs and potential gains surrounding CSR
- Management attitudes, i.e. reluctance to implement strategies that may not reap financial benefits for the firm or its owners
- Conflicting stakeholder interests, e.g. shareholders are likely to place profits before ethics
- Those firms that do not comply may, by default, gain a price advantage
- The opportunity costs involved, i.e. what else the firm could have done with the money used to implement CSR policies.
(b) The question requires candidates to discuss whether Walmart’s practices are morally acceptable. Thus, a two-sided argument should be provided. On one hand, some would argue that Walmart make sufficient profits to be able to refrain from damaging the environment and exploiting workers. However, others would argue that it is not the role of a private sector business, owned by shareholders, to protect the environment.
It is also difficult to place a realistic value on the environment and to measure the relative financial benefits of environmental protection versus profits. In particular, shareholders and investors may well question the value of environmental conservation. By placing profit maximization as its key objective, Walmart is more likely to be able to expand and be in a better financial position to look after its employees.
Nevertheless, reasons why Walmart might consider its CSR ahead of its profits include:
- Walmart has already been fined millions of dollars by the US government due to its unethical business practices; so perhaps it is worthwhile to take CSR more seriously.
- The claim that up to 8% of its customers boycotted the company suggests that Walmart can no longer ignore the claims being made in the media.
- A staff turnover rate of 70% is not sustainable in the long run.
- Negative publicity might cause major global repercussions for the high-profile multinational corporation.
Ultimately, the moral dilemma is a subjective one. In order to answer the question, it depends on whose point of view we looked at. Employees will most certainly agree that their wellbeing should be the key objective, whereas shareholders and directors may think differently. It is, after all, the case that not acting ethically does not mean that the firm is necessarily being unethical.
Question 5

Answer
(a) Limited competition in a niche market – this is likely to be an opportunity for Kidzplay Bouncy Castles. This is because competition is an external factor and since the business operates in a niche market, there are opportunities for expansion without the threat of intensive competition.
(b) Limited business on its newly launched website – this might be considered as a weakness as the factor is, to a large extent, within the control of the business. Kidzplay Bouncy Castles could take a more proactive approach to the online promotion its business.
(c) Struggling to recruit suitable staff – again this could be seen as a weakness because the firm is unable to hire the right staff. Perhaps there is a need for Kidzplay Bouncy Castles to review its workforce planning and remuneration package.
(d) Demand in the winter months is weak – this might be perceived as a threat since seasonal fluctuations in demand caused by the weather is beyond the control of the business. Poor weather during the winter in the UK is likely to dampen the demand for the services provided by Kidzplay Bouncy Castles.
(e) Highly profitable earnings could attract competitors – this is a potential threat to the business since competitors are attracted by the high earnings potential. With a greater number of rivals, Kidzplay Bouncy Castles is likely to lose some market share.
Question 6

Answer
(a) Market penetration (Cadbury’s trying to capture a larger share of the market) or product development (new products being launched in existing markets).
(b) Product development (new products by Nissan in an existing market for luxury cars).
(c) Product development (new products to existing Tesco customers) or diversification (as Tesco has expanded to provide petrol and financial services which are not part of its core competencies).
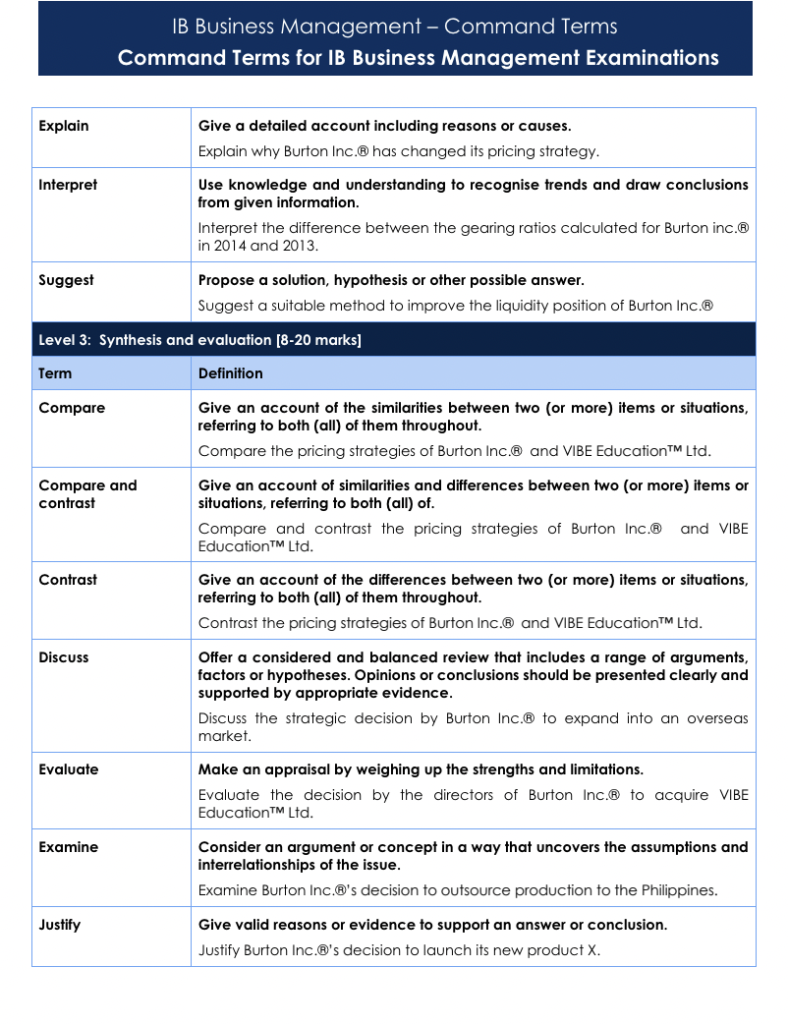
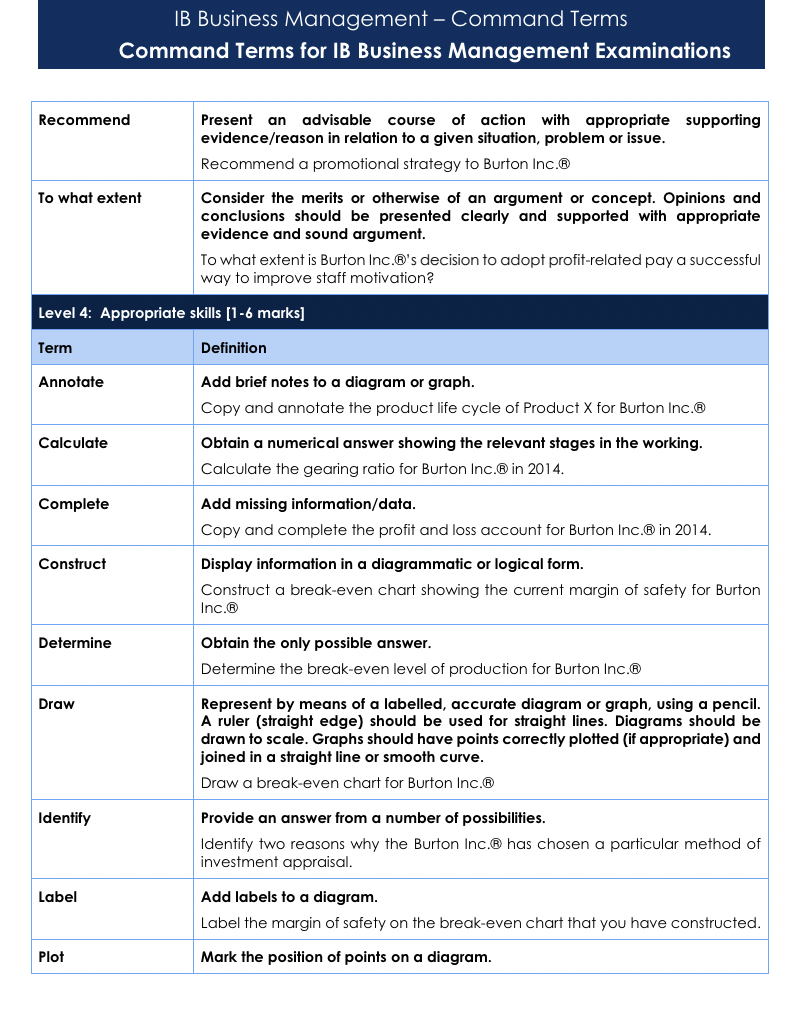
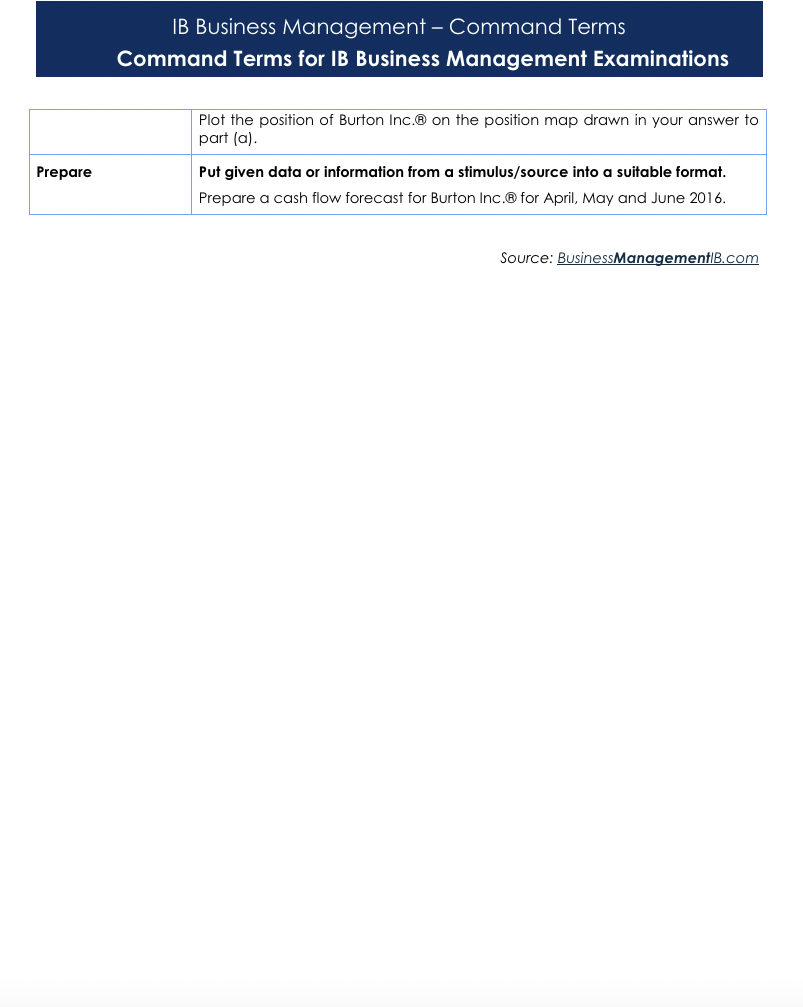
Command Terms
References
- https://ebooks.papacambridge.com/viewer/ib/group-3-individuals-and-societiesbusiness-management-ibid-business-management-paul-hoang-third-edition-ibid-2014-pdf
- https://ghcc.org/en/5-steps-to-set-smart-objectives-examples/
- https://corporatefinanceinstitute.com/resources/management/ansoff-matrix/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SWOT_analysis



