Table of Contents
- I. Dispersion of Light
- II. The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- III. Uses of the Electromagnetic Waves
- IV. Harms of Radiation
- V. Light in Vacuum
Hello readers! It’s Zahra, and we’ll be reviewing the IGCSE Physics topic: Electromagnetic Spectrum. Here, we will be going through the important key concepts for your better understanding.
Take a look at the picture below:
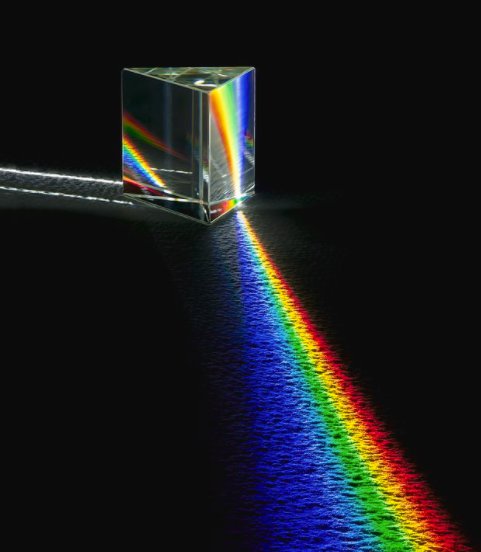
I. Dispersion of Light
As seen in the image above, the white light refracts and leaves the glass, splitting it into a spectrum of colours. This splitting up of white light into a spectrum is known as dispersion; meaning ‘to spread out’.
As white light enters the prism, it slows down. We say the light is refracted because it changes direction. Dispersion occurs because each colour is refracted by a different amount. The following spectrum of visible light displays the colours (in order) red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. Learn more about this phenomenon in this source guys! It expands beyond the syllabus but it’s quite an interesting!
II. The Electromagnetic Spectrum
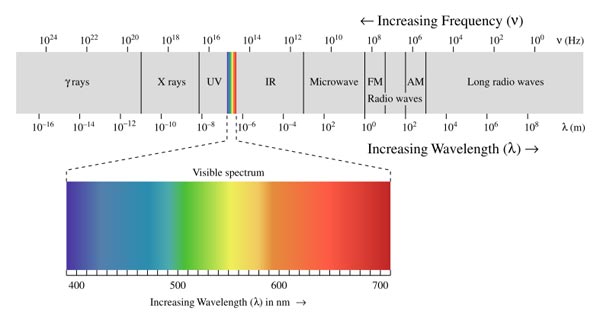
Remember this helpful mnemonic:
“Real Madrid Is Losing Under Xavi’s Goals”
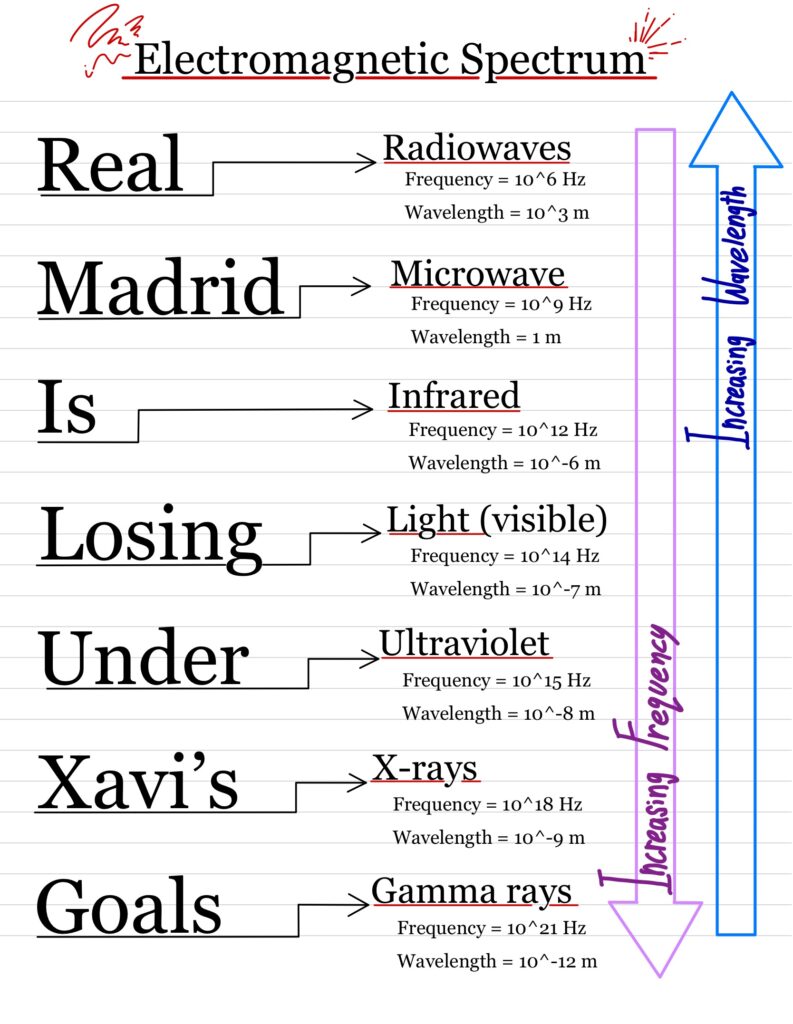
III. Uses of the Electromagnetic Waves
There are many ways we make use of these waves in our world today. Here are some important examples!
- Radiowaves: Broadcast radio, astronomy and television signals.
- Microwaves: Satellite communication, mobile phones, Bluetooth and microwave ovens.
- Infrared: Household electrical appliances, remote controllers, intruder alarms, thermal imaging and optical fibres.
- Visible Light: Photography and vision (during daylight).
- Ultraviolet: Sunbeds to provide sun tan, security marking, detecting counterfeir bank notes, sterilising water.
- X-rays: Hospital use in medical imaging, security scanners, killing cancerous cells, engineering applications (such as detecting cracks in metal).
- Gamma rays: Medical treatment in detecting and killing cancerous cells, sterilising food and medical diagnosis.
IV. Harms of Radiation
Exposure to these electromagnetic waves can do some real damage that you may or may not have heard of. H are the list of the following hazards:
- Microwaves: Internal heating of body cells.
- Infrared: Skin burns.
- Visible Light: Bright light shone into eyes can cause blindness.
- Ultraviolet: Damage to surface cells and eyes, leading to skin cancer and eye conditions.
- X-rays & Gamma rays: mutation or damage to cells in the body.
V. Light in Vacuum
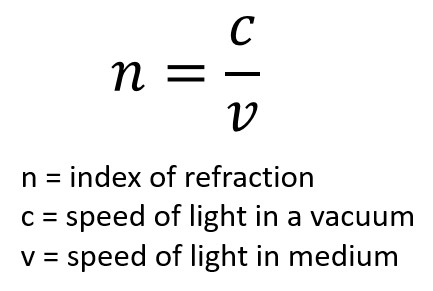
C refers to the speed of light in vacuum, 3*10^8 m/s.
Sample Question
“A light ray has a speed of 2*10^8 m/s when travelling through a glass block. What is the refractive index of the glass block?”
ANSWER:
(3*10^8) / (2*10^8) = 1.5

Hey buddy! 😉 You’ve made it to the end!! I hope the information above will be a useful source for your knowledge on forces. If this helps, then sure to check our other blogs related to the physics topic, here. Thanks for reading, and good luck on your studies reader!



