Here is a 101 lesson on IB Business that might help you!
Firstly, getting used to your terms will be super helpful while reading.
Glossary:
Consumers: People & organisations who are willing and able to buy goods and services
Consumption: Using up goods and services to satisfy consumer’s needs and wants
Production: Using resources to make goods and services to satisfy consumer’s demands
Producers: People & organisations who are willing and able to produce goods and services
Output: The final products or services produced by a business or economy.
Input: The resources and factors used in the production of goods and services.
Profit: The financial gain when revenue exceeds production costs.
Factors of Production: Resources like land, labor, capital, and entrepreneurship used in production.
Processes: The methods and steps for creating goods or services.
Table of Contents
- 1.1.1 The nature and role of business
- 1.1.2 The Doughnut Economics Model
- 1.1.3 The Economy
- References:
What is a business?
It is an organisation that uses resources to meet the needs and wants of customers by providing a product or service that they demand usually with the aim of making a profit.
1.1.1 The nature and role of business
Businesses work as systems, with a infinite flow. It all starts with input.
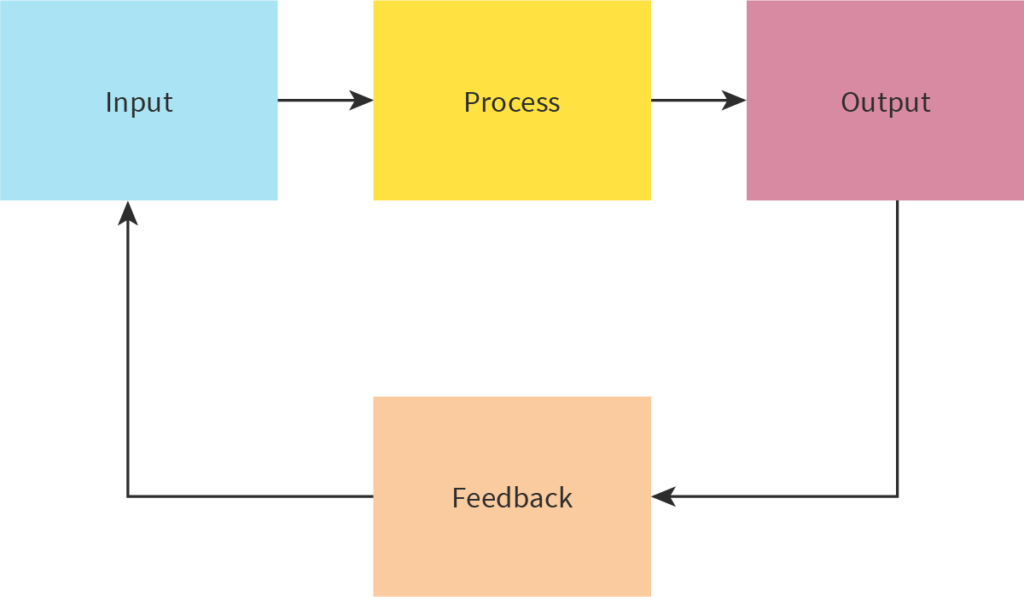
Inputs are the resources needed to create a product or fund a service operation.
There are 3 types of inputs: Physical, Financial and Human inputs:
Physical resources are raw materials and semi-finished goods that businesses need to produce. Raw materials are agricultural products such as wood, metals and oil. Semi-finished goods (also called intermediate goods) are goods that have already been processed or produce, but not exactly consumer products. They might be the electronic components that are purchased by companies to then be assembled with other semi-finished products.
Capital goods are machinery and equipment used in the production process. These can be computers or robots needed to produce goods.
Financial resources are the funds that businesses need to start up. They are used to grow and maintain the business for the long run. Medium-term or long-term financing is when businesses borrow large amounts of money for a longer time (typically more than 1 year) to buy business’s physical inputs (usually to purchase property). There are also short-term financing, which are small scaled funds needed to pay for the inputs that will soon be processed and then sold by the business. These items are usually called stock/ inventory where businesses has in storage. This is usually needed to pay for things such as short term loans, monthly payments and employee salaries.
Human resources are the people involved in the business needed to run the operation. They usually consist of mainly managers and employees. The element of enterprise is the process of taking risk and combining resources together to create goods and services.
Factors of production:
– Land: Natural resources
– Labour: Human resources
– Capital: Physical and financial resources
– Entrepreneurship: Taking risk and combining resources together to create goods and services.
Processes
| Function | Processes |
| Human resources management | Process that ensures that the business employs the correct number of employees skilled to produce and deliver its products or service. This process ensures that employees are treated ethically and keep in touch with the right laws. |
| Finance and accounts | Process that ensures that the business has the right amount of money needed to maintain the business to carry out till the future. |
| Marketing | Process of selling the product or service at the right price, right time and right customers. |
| Operations | Process of how the core activity of the business is carried out. They must plan how and how much is goods and services needed to be produced. Ex: Building property, growing crops, selling products, etc |
Outputs
Goods are tangible objects, meaning they are physical (can be touched) and can be measured. Examples: Chocolates, paper, cars.
Services are intangible objects, meaning they cannot be touched or described by physical characteristics. Examples: Health care, education, haircut.
Feedback
It is the process where the output of a system becomes an input to the same system.
Negative
When the output feeds back into the inputs in a way that moves the system in the opposite direction.
Ex: Feedback on schoolwork can help you improve it.
Positive
Occurs when the output feeds back into the inputs in a way that moves systems and processes in the same direction.
Ex: Bad school evaluation might demotivate you and lead to lower-quality work.
1.1.2 The Doughnut Economics Model
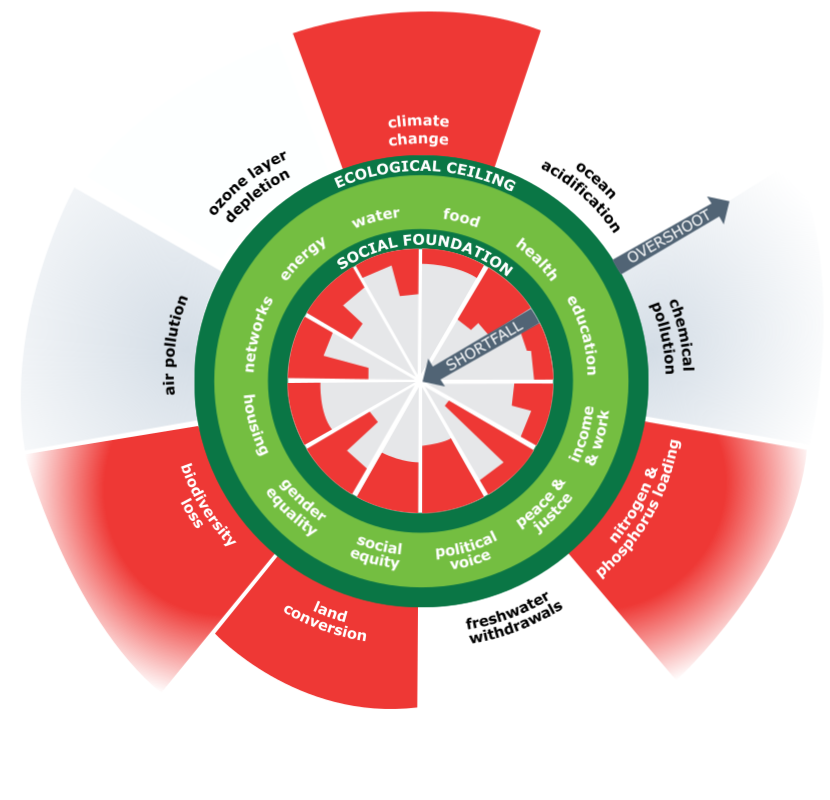
Planetary boundaries / Ecological ceiling
The Doughnut Economics Model’s outer ring is environmental. Important natural systems work together to sustain life on Earth. The outside ring of the model shows fresh water, land, and atmospheric systems. But people constantly disrupt these systems. Too much disruption can cause permanent damage to Earth’s systems. Damage can render the planet unlivable. These systems’ limitations are planetary boundaries or ecological ceilings.
The red area indicate that humans are overpressing numerous Earth systems. Climate change, biodiversity, land usage, and agricultural fertiliser nitrogen and phosphorus flows.
Human needs / Social foundation
Production and consumption of products and services that fit human needs and wants strain Earth’s systems. The inner ring of the Doughnut Economics Model represents human wants or the social foundation, Which are food, water, and shelter. Social interaction needs include human networks, social equality, political voice, and work. Red parts in the inner circle indicate global human needs unmet. Hovering over them provides more information.
The goal is to provide human needs while protecting the environment. It indicates entering the green safe space.
We are not there yet. We are not addressing human needs or protecting the environment globally. We consume too many resources and don’t use them efficiently to meet human needs. Then the Doughnut model is red inside and out.
In the Doughnut Economics Model, you can see how each country is serving human needs and protecting the environment.
Businesses are crucial to meeting human needs while protecting the environment. Human needs should be provided by more than just social enterprises’. All businesses should evaluate their products to see if they benefit human lives.
1.1.3 The Economy
An economy is a system for producing and distributing goods and services amongst a group of people.
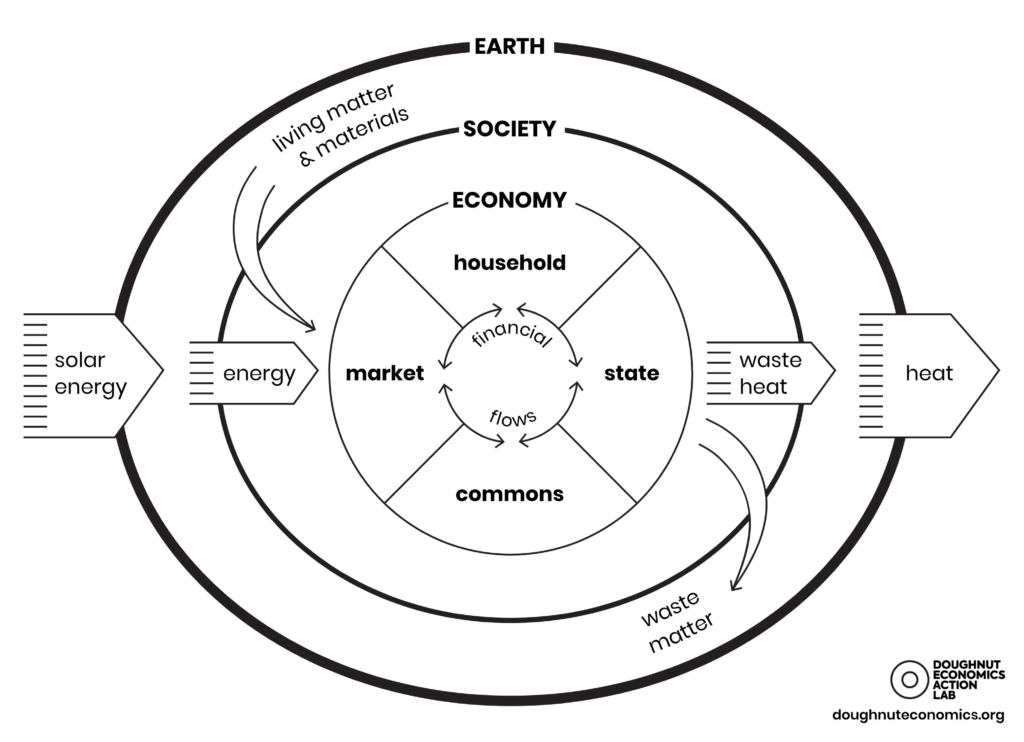
This is an economic model. All life and human activity are on Earth. Humans’ needs and wants are met by society and the economy using Earth’s resources. Social and economic integration into nature is crucial. Understanding that we depend on Earth’s resources is crucial.
Distribution systems and groups are shown in the model’s center:
Households—strong relationships give vital care. These goods and services are mostly made by unpaid labor.
Government: offers essential products and services to everyone. Goods and services are generally free or cheap. Their main funding source is taxes.
Common Resources – supplies society’s products and services or natural resources. People self-organize commodities, services, and resource distribution. Nothing is paid.
Market sell business products. Businesses make and sell products and services for money.
Needs and wants can be met in numerous ways. Many organizations, including corporations, meet human needs and wants.
The course emphasizes markets and the state. However, households and the commons are crucial to providing human needs. When enterprises, the state, households, and the commons collaborate, economies improve.
Sectors of the economy
Primary sector
The primary sector extracts raw materials from the Earth. Primary sectors include agriculture, fishing, forestry, mining, and drilling.
Secondary sector
The secondary sector manufactures and processes the raw materials, which is then made into products for sale. Examples are carmakers, food processing companies, chemical businesses and phone production.
Tertiary sector
The tertiary sector refers to service-based firm. Selling clothing, food, education, healthcare, legal services, travel, and transportation are tertiary sector enterprises.
Quaternary sector
The quaternary sector is new. It focuses on knowledge-based services. Quaternary services could be termed tertiary. Over the past 50 years, new enterprises have focused on gathering, processing, and selling data. Web-based and new media companies are considered in the quaternary industry.
Relationship between sectors
The primary sector involves getting resources from nature, like farming or mining. The secondary sector is where those resources are turned into things we use, like factories making cars from metal. The tertiary sector is about providing services, like teachers, doctors, or people in tech support. These sectors work together to make a country’s economy strong, with the tertiary sector often supporting the other two as the economy becomes more advanced.
Check out other blogs in the site!
https://prodatblog.org/business-management-experience/



